Technology Offers Site map description
N
 Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)
Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Research Institute
Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST) posted this:
Non-lethal system for surveying and/or monitoring animals and in particular flying insectsThe invention aims to improve the taxonomic resolution of image-based determinations of individual insects or other small invertebrates by recording multiple-view images of single individuals. A small camera is connected to a micro-computer which is programmed to take high-resolution images of the reflections of an individual specimen (e.g. an insect) through a mirror system, showing different angles of view. The imaging device is connected to an entomological trap adapted to direct the intercepted or caught individual towards the entrance of the imaging device. The images are recorded as the individual insect or other small animal traverses the device, after which it escapes unharmed .Barry McGraw posted this:
Non-Phosphorus Soy-Based Scale Inhibitor for Water Treatment Systems (e.g., oils wells)Airable Research Lab, in partnership with LFS Chemistry, has developed a non-phosphorous alternative to its soy-based scale-inhibiting additive. The scale inhibition industry has been historically dominated by phosphorous-based chemistries. Currently, overexploitation of phosphorous—along with a pandemic, geopolitical disputes, trade wars, and escalating fuel prices—has limited access to the element and driven up prices. In addition, phosphorus in our waterways lead to eutrophication, a serious form of water pollution. Airable’s renewable, phosphorous-free solution conserves and preserves our natural resources, with a scale inhibition efficiency of up to 90%.
CEO at Airable Research Lab, business line of Ohio Soybean CouncilJuan Casado posted this:
Non-Thermal Method for In Situ Regeneration or Cleaning of Activated CarbonAn alternative chemical method for regeneration of activated carbon at room temperature consisting in the in situ combination of a diluted acid and two oxidants with a catalyst for the desorption and oxidation of pollutants previously adsorbed on carbon material. This so called CARBOX technology is less expensive than state-of-the art thermal regeneration of activated carbon since no energy input is required.
R&D Manager at UAB Servei de Gestió de la InnovacióUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPCServei de Gestió de la Innovació
Servei de Gestió de la InnovacióUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPCServei de Gestió de la InnovacióLicensing Manager at Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC
View ProfileServei de Gestió de la Innovació posted this:
Non–invasive method for the objective assessment of the intraocular scattering of the cornea and the crystaline lensA new method has been developed for the assessment of the intraocular scattering generated in each structure of the human eye, i.e., the cornea and the crystalline lens. Based on a non-invasive recording of images of the light reflected on the different surfaces of the eye (Purkinje images) and their posterior image processing allows the objective assessment of the intraocular scattering of the cornea and the crystalline lens separately. It is a simple and cost-effective method easy to use in clinics.
Licensing Manager at Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPCUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
Novel 3D-polymeric monolithic catalystResearchers from Inorganic Chemistry Department at the University of Alicante have developed a new procedure to obtain heterogeneous monolithic catalysts with polymeric support that allow to accelerate catalytic reactions in an optimal way at moderate temperatures, being especially suitable in Preferential Oxidation of Carbon in Hydrogen Rich Gases (CO-PROX). These novel catalysts have been manufactured by 3D printing with complex geometries, improving the performance of current supports. These heterogeneous catalysts are characterized because they have similar conversion and selectivity profiles to current unsupported powder catalysts. They have increased catalytic activity during prolonged reaction times and greater resistance to friction wear. We are looking for companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
Novel acoustic wave device and filter for its use in high frequency applicationsAn acoustic wave device with one or more dielectric compensating layers that compensates the spurious signals by substantially temperature-independent nonlinearities occurring within the device has been developed. A direct application of this device has been the development of a novel acoustic filter. Partners to further develop the system and/or to establish commercial agreements with technical cooperation are sought.Covid-19 Innovation Challenges by Innoget posted this:
Novel Activating Antibodies for Viral TreatmentNovel Activating Antibodies for Viral Treatment Various pathogens (bacteria and viruses as well) bind to specific cell adhesion molecule in order to inhibit the immune response and/or to infect the host cells. However,upon binding and induction/activation, the cell adhesion molecule suppresses virus production by an SHP2-dependent process which involves also suppression of mTOR-mediated protein biosynthesis. Project ID : 47-2020-10898Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
Novel actuation system for an active orthosisA novel actuation system for a knee orthosis has been designed and patented. This new technology allows to actuate or lock knee rotation during gait, by means of a single motor and a ball-screw transmission. The system is lowweight, compact and easy to adapt to commercial passive orthoses. Partners to further develop the system and/or to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.Universidad de Alicante posted this:
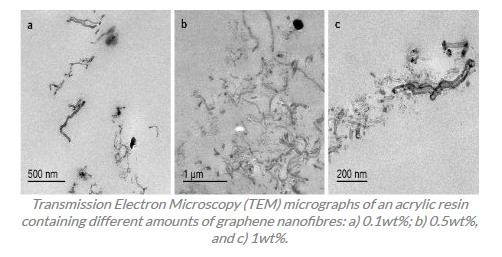
Novel and simple procedure for dispersing graphene derivatives in chemically curable resins.The Laboratory of Adhesion and Adhesives of the University of Alicante and the company Dental Global Training, have developed a new procedure to incorporate efficiently graphene derivatives (nanofibers, nanosheets, nanoparticles) in chemically cured resins by using an in situ polymerization technique. The method is very simple and fast, it provides an excellent dispersion of the graphene derivatives in both the solid components of the resin and in the cured polymer matrix, and is entirely friendly with the environment. The novel method does not require the use of organic solvents nor water, ultrasounds, and high pressure/temperature. The resulting resin composites show excellent mechanical properties, good wear resistance, easy manipulation and increase the insolubility in oral fluids, and therefor they have special interest in applications in odontology, traumatology and non-medical applications too (automobile, construction, civil engineering, aeronautics, space engineering, electronics and optics). It is looking for companies interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation.Solomon Rosenblatt posted this:
Novel Antimicrobial Based on Control-Release IodineA novel class of iodine technology has been developed producing iodophors in many product forms that control release iodine in minute, biocompatible quantities resulting in sanitizing products with superior biocidal efficacy, and lower toxicity than many traditional biocidal agents. Iodine is of natural origin and already present in our bodies.
Biomedical ChemistKirsty Smitten posted this:
Novel Antimicrobial Materials, with Broad-Spectrum Activity and Applicability in Medical and Non-Medical ApplicationsMetallobio are developing novel antimicrobial additives. The additives modular synthesis makes this platform technology applicable in many different fields. The additives exhibit broad-spectrum activity against a range of planktonic and biofilm forming bacteria including World Health Organisation Priority Pathogens. Metallobio have incorporated these additives into a range of materials including polymers and commercial latexes. The antimicrobial materials have good durability and a high antimicrobial efficacy.
CEO at MetalloBio LimitedLucas Montes Pérez posted this:
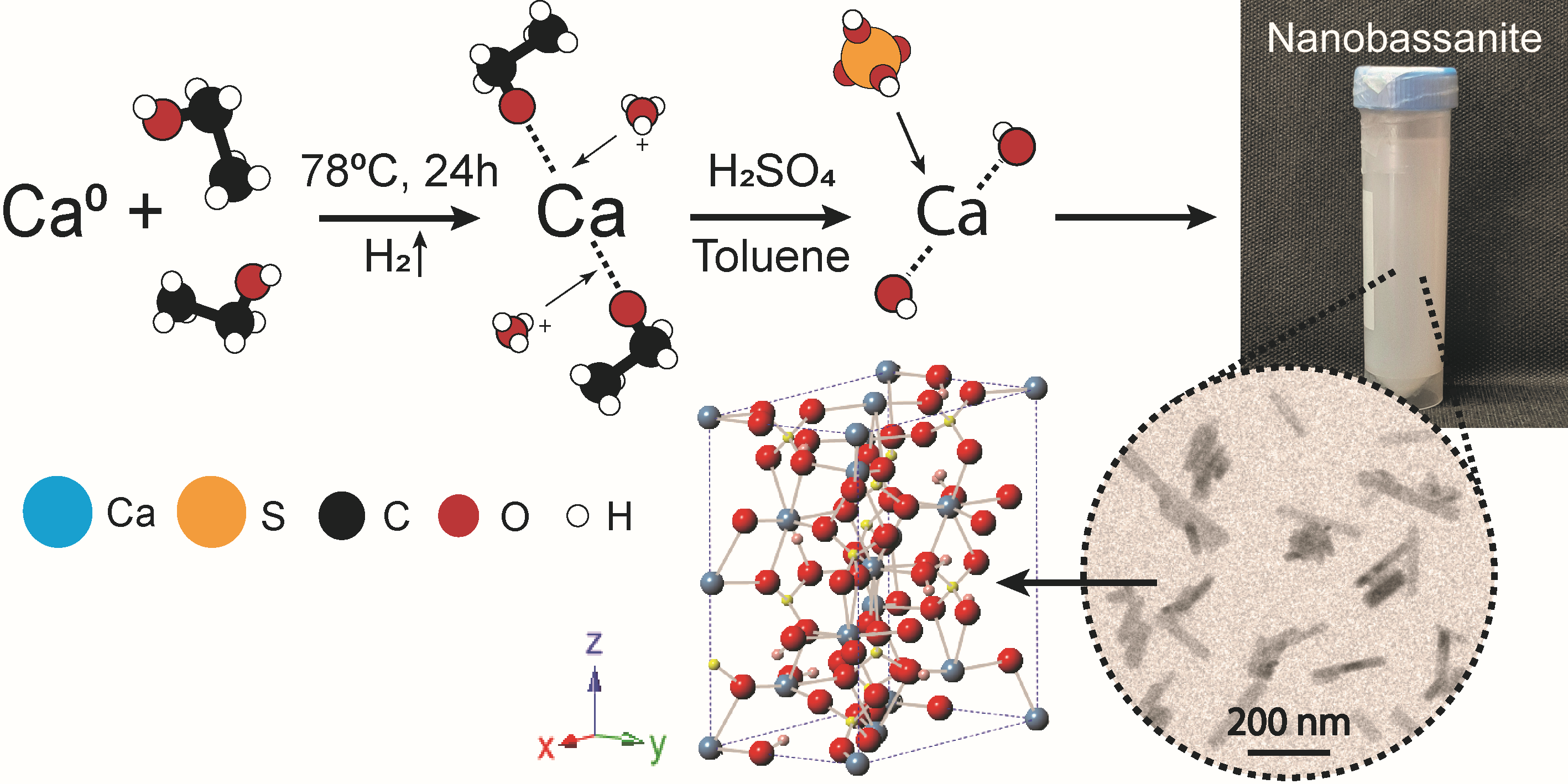
Novel bassanite nanoparticles production methodA new efficient, simple, selective and no-byproducts method for the synthesis of basanite nanoparticles has been developed. Its application will meet current needs associated to the production of these nanoparticles, which can be used in different sectors such as heritage restoration, construction or biomedicine.
Licensing Manager at Universidad de GranadaJavier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
Novel bioadhesive for wound closure in animals or humansThe Adhesion and Adhesives Laboratory research group has developed a new biomaterial for use as adhesive or tissue sealant applicable to both animals and humans. This invention solves the disadvantages of the adhesives known so far presenting optimal properties such as biocompatibility with living tissues, high adhesive capacity, adaptable to the tissue of the wound being bond, absence of toxicity and tissue regeneration properties. The group is looking for companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation.
Universidad de AlicanteUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
Novel biobased aromatic and aliphatic polyesters from carbohydratesNew biobased aromatic and aliphatic polyesters that can replace isosorbidebased polyesters with improved properties (mechanical, thermal, optical and chemical resistance) have been patented. Partners to further develop the system and/or to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.Meghan Meyer posted this:
Novel Biodegradable Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer' Provides early detection of pancreatic cancer, significantly increasing the potential for successful treatment outcomes ' Utilizes targeted nanoparticles, enhancing specificity and reducing false positives in diagnostic imaging ' Supports the development of personalized medicine approaches by enabling precise lesion targeting
Other at Georgetown University Alexander KvashninInstitute of Computational Technologies, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of ScienceAlexander Kvashnin
Alexander KvashninInstitute of Computational Technologies, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of ScienceAlexander KvashninInnovation Manager at Institute of Computational Technologies, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Science
View ProfileAlexander Kvashnin posted this:
Novel biomass converter for smart agriculture with adaptation of the technology to the Southern Europe through Italian-Russian partnershipRussian engineering company has developed and patented a novel biomass converter for processing biomass and carbon containing wastes with generation of heat, energy carriers and fertilizers. The technology uses filtration combustion with superadiabatic heating and processing of materials in fluidized bed. The biomass converter can be used to process different carbon containing materials of natural and technological origin (e.g., wooden chips, wood processing wastes, agricultural wastes, textile production wastes, packaging, paper-making, cellulose, municipal wastes, etc.). The company field-tested the technology by processing very complex wastes such as poultry droppings (including wastes from broiler chickens raised in cage chicken houses), cattle manure, straw, wastes from seed oil production, wastes coal from refining. The biomass converter can produce heat, biocoal, and ash. This means that the companies using this technology can earn revenue from processing wastes, generating power stored in biocoal as well as from production of mineral fertilizers in the form of ash. There are different designs of a biomass converter depending on the type of wastes to be processed. The partnership may be developed within the project that in its own turn is dedicated to adaptation to the South European sources of biomass and streams of carbon containing wastes of an innovation equipment and method developed and patented by the Russian partner. The project will involve identification of biomass sources in the Southern Europe, primarily Italy by the conditions in which biomass is produced, by kinds of wastes, amounts of wastes, location of sources of wastes, location of consumers of biocoal and fertilizers and other factors. The project will result in a newly designed biomass converters each of which can be installed as nodes into a distributed network of alternative energy sources based on biomass. The equipment will have high potential for commercialization in Southern Europe and Russia. Pilot processing station will be built for demonstration and further commercialization in Italy.
Innovation Manager at Institute of Computational Technologies, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of ScienceUniversity of Waterloo posted this:
Novel coaxial tunable bandpass filterBackground Tunable bandpass filter is one of the vital components of frequency reconfigurable (or frequency agile) wireless systems which facilitate effective utilization of allotted frequency spectrum. Frequency reconfigurable wireless systems can be a cost effective solution for wireless base-stations as well as for satellite & aero-space applications. In satellite application, on orbit flexible payload (or programmable payload) is one such encouraging development on the horizon. These systems inevitably require high Q (Quality factor) tunable bandpass filters with a constant absolute bandwidth over the tuning range. One of the important requirements for tunable filters in most applications is to maintain constant absolute bandwidth over the tuning range. The data rate is bandwidth dependent thus maintaining the same data rate over the tuning range requires maintaining the same bandwidth. In addition, most of communication system applications require maintaining certain isolation requirements outside the band, which cannot be satisfied if the bandwidth is changed. Thus, by maintaining a constant bandwidth over the tuning range, the achievable data rate and the filter isolation requirements remain the same over the entire tuning range, which is highly desirable.Yeda posted this:
Novel Combination Therapy For Improved Management of DepressionPsychiatric disorders, especially major depressive disorder (MDD), are leading causes of disability and premature death across the globe, with patients showing a heightened risk of self-harm and suicidal ideation. Prof. Alon Chen and his team found that the sustained antidepressant effects of Ketamine, an approved drug indicated for treatmentresistant depression, are mediated by the upregulation of the Kcnq2 gene. The team found that combination therapy comprised of Ketamine and retigabine, an approved KCNQ agonist, boosted the anti-depressive effects of Ketamine in mice. Therefore, the novel combination treatment of two approved drugs, Ketamine and retigabine, may improve current treatment protocols for psychiatric disorders, including depressive disorders MDD.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
Novel conic cannula for spine cement injectionNovel conic cannula for homogeneous injection of bone cements in the spine have been patented and developed. The new design is especially indicated for the injection of ceramic-based bone cements because the pressure drop developed along the cannula minimizes bone cement’s press filtering. Partners to further develop the technology and/or to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.Georgetown University posted this:
Novel Crystalline Cavitands for Gas Separation and Storage- Novel crystalline cavitand compositions with unique void spaces for efficient gas separation and storage. - Utilizes molecular/organic synthetic chemistry to enhance synthetic variability and efficacy in industrial applications - Versatile applications extend beyond gas separation, offering potential solutions for diverse industrial needs such as catalysis and ion exchangeCINBIO posted this:
Novel derivatives of psammaplin A, a method for their synthesis and their use for the prevention or treatment of cancerThe object of the invention is to obtain new molecules with a structure analogous of psammplin A and significant biological activity on cancer cell lines. Therefore, a method has been developed for the synthesis of new molecules with properties such as inducing cell cycle detection, apoptosis and acting as inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDACs), among others. In addition, they serve as intermediates for the synthesis of more biologically active molecules and the development of new drugs.Universidad de Alicante posted this:
Novel device for simultaneous determination of adsorption of binary gas mixtures on solid adsorbents• This system is thermostated and temperature can be adjusted to the desired experimental conditions. • It is possible to implement in the volumetric device other suitable elements to determine density (e.g., elements based on measurement of resonant frequency, and so on).Innoventions Ltd. posted this:
Novel Emboli Capturing and Removal Double-Filtering System for Whole-Body Prevention of Embolic Complications During and After TAVI / TAVR ProceduresInnoventions' proprietary novel Emboli Capturing and Removal Double-Filtering System, integrated to TAVI/TAVR delivery system is for total double-filtration and collection of the embolic particles during the procedure and removing them from the body a the end of the procedure. Differing from the current emboli deflection devices which deflect the embolic particles for preventing cerebrovascular embolic complications, our device prevents dispersion of the embolic material and prevents them reaching all body organs. As such, with our device we are bringing a much more secure and effective solution than the currently used devices.Georgetown University posted this:
Novel Fluorescent Compound for Treating Prostate Cancer by Restoring RASSF1A Expression- Innovative dansyl-carbazole compound effectively restores RASSF1A expression, potentially inhibiting cancer cell proliferation in androgen-independent prostate cancer - Fluorescent compounds enable intracellular visibility, facilitating targeted therapy and monitoring of treatment efficacy, offering a significant advantage in cancer treatment - Beyond prostate cancer, the invention addresses various cancers with decreased RASSF1A expression, providing a versatile cancer cell identification and treatment solution Gerard SisóUniversitat Autonoma de BarcelonaGerard Sisó
Gerard SisóUniversitat Autonoma de BarcelonaGerard SisóGEMMA-CIMITEC Group Research and Innovation Promoter at Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona
View ProfileGerard Sisó posted this:
Novel highly-sensitive microwave sensors for dielectric characterizationMicrowave technology is of special interest for the implementation of low-cost, low profile, and highly sensitive planar sensors devoted to the analysis of material properties. Microwave sensors exhibit a wide range of potential applications, in so many different fields such as health/veterinary (monitoring of electrolyte concentration in blood or urine), industrial processes (fermentation monitoring, liquid concentrations, cleaning processes monitoring…) or construction (defect detection in infrastructures), among others. The main characteristics that make this sensor technology competitive are the high sensitivity and the possibility of real-time monitoring, the latter being very important since it offers the chance to save time and resources that could be critical in some industries
GEMMA-CIMITEC Group Research and Innovation Promoter at Universitat Autonoma de BarcelonaUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
Novel individualized, homogeneous and adjustable lighting system for animalsThe Neurobiology of the Visual System and Therapy of Neurodegenerative Diseases (NEUROVIS) research group at the University of Alicante has developed a comprehensive lighting system for housed animals that can be self-regulated in an individualized and automated way, depending on the specific lighting conditions of the space or module in which each animal is located.Michael Locker posted this:
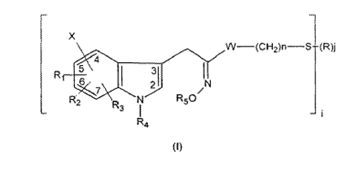
Novel KRAS G12C agent with improved potency & PK properties availableAgent being offered has almost 5x greater binding and 2.6x higher potency than AMG510. Additional data available upon sincere requests. Please contact me with serious interest only.
ShamRock PharmaceuticalsCSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
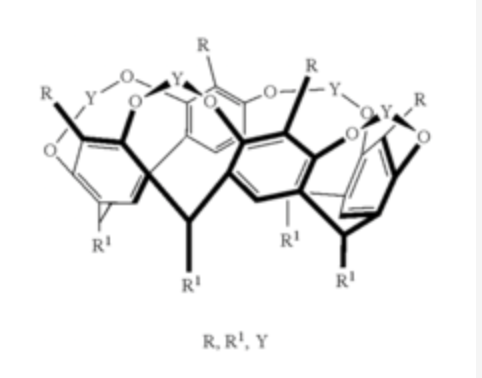
Novel luminescent probes of lanthanide complexes for sensing of biomoleculesCSIC and Universidad de Granada have developed a new family of antenna chromophores able to sensitize effectively luminescence of lanthanides to be applied as labelling probes for biomolecules. Industrial partners specialized in fluorescent probes for biological research are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement.Universidad de Granada posted this:
Novel luminescent probes of lanthanide complexes for sensing of biomolecules.A research institution and a university from Spain have developed a new family of antenna chromophores able to sensitize effectively luminescence of lanthanides to be applied as labelling probes for biomolecules. Industrial partners specialized in fluorescent probes for biological research are being sought to collaborate through a patent license agreement.Sayali Warad posted this:
NOVEL METHOD FOR CRYO-PRESERVATION OF CELLS IN MONOLAYERSPreserves cells on a substrate and provides high post-thaw cell viability Cryopreserved cells are ready for immediate use for modeling human diseases, drug screening, research applications
IP Market Analyst at University of Alberta, Technology Transfer Services