Technology Offers Site map description
A
ALL Chemistry Inc. posted this:
ALL Chemistry Inc.'s High-Throughput Screening ServiceALL Chemistry's compound screening platform provides both phenotypic and target-based methodologies. Our capacity reaches approximately 100,000 sample screenings per day. Customers only need to hand over the compound library to us, and we will screen potential compounds through standard experimental procedures.Laser Consult Ltd. posted this:
All-natural hydrophobic oil absorbent powders and granules for environmental & industrial purposesThe technology consists of an original industrial process by which natural materials can be turned into products with hydrophobic oil adsorbent properties. The captured oil can be extracted and recycled, and the product can be reused several times over. These products can be developed as powders or granules with varying levels of hardness, water resistance, size, and density for diverse set of applications.Yeda posted this:
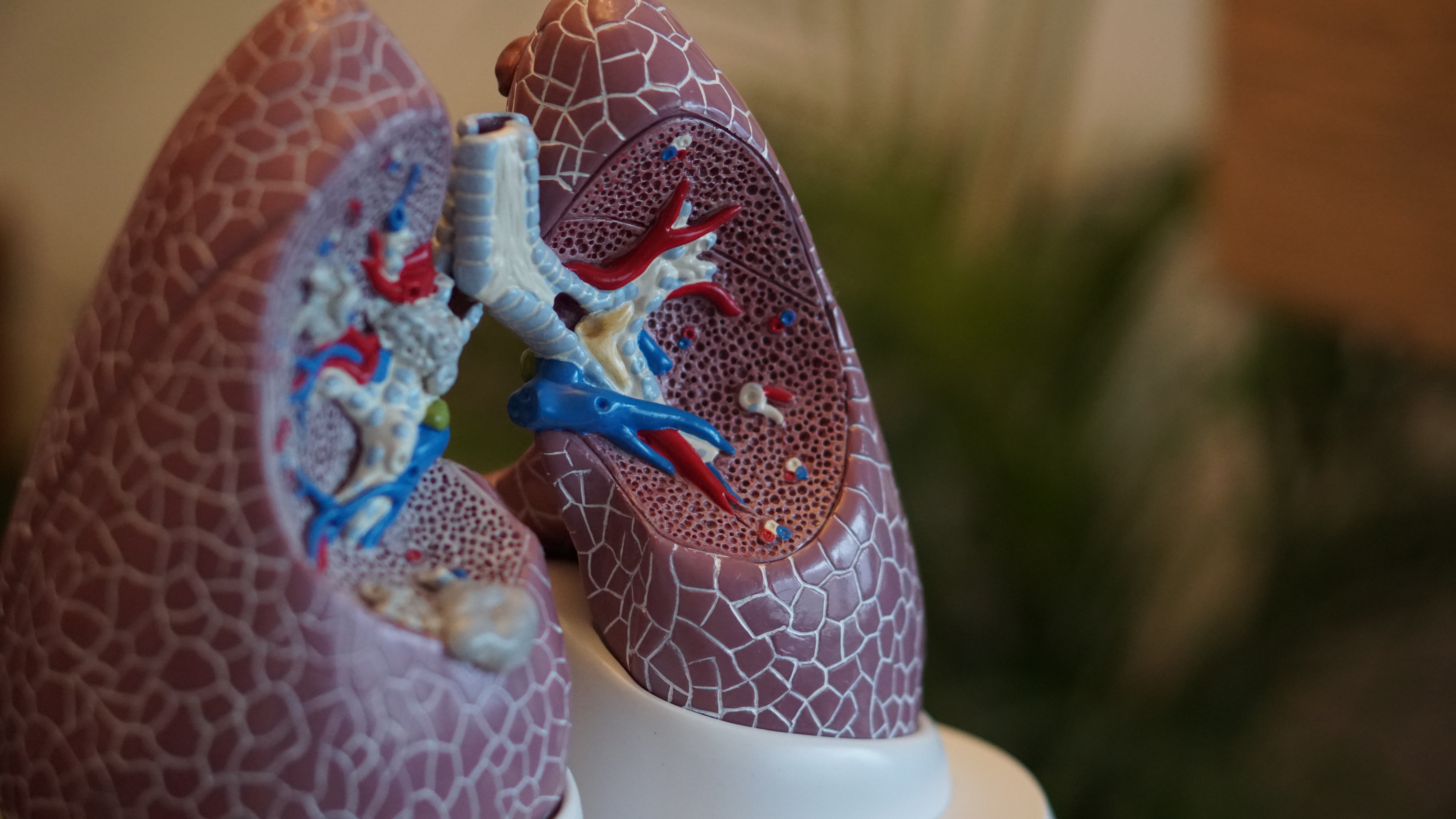
Allogeneic Cell Transplantation for Treatment for Lung DiseasesThe treatment of respiratory conditions is currently one of the major challenges to health care systems all over the world. The problem is that most therapeutics currently available for treating pulmonary indications are non-curative, and simply improve symptoms. Presently the only cure for late stage pulmonary diseases is a lung transplant, which includes its own host of problems ranging long waitlists to lifelong immunosuppression. These issues explain why pulmonary diseases represent the second leading cause of death in the world. Therefore, a strong need exists for alternative therapeutic options in treating pulmonary related diseases.Prof. Yair Reisner and his research group have developed a unique set of methods for culturing and transplanting cells for use in treating respiratory illnesses. Their innovation was not simply an improvement in terms of symptoms but actually showed effective lung repair in mouse models.Alpha Lifetech posted this:
Alpha Lifetech-Phage Display For Antibody DiscoveryAlpha Lifetech can provide a wide range of services for phage display antibody development. The main services include: the VHH antibody library platform, scFv antibody library platform, Fab antibody library platform, phage library construction platform, phage library screening platform antibody humanization service, and other services.
R&D Manager at Alpha Lifetech Inc.Pascal Mayer posted this:
Alphanosos - Leader in botanical plant-based natural antimicrobial control, well-being and medicineAlphanosos is active in animal feed, medical foods, and pharma, and with the right venture partners, to become a leader in botanical plant-based natural antimicrobial control, well-being and medicine through its R&D based on proprietary Artificial Intelligence. Alphanosos’ first patent-pending discoveries are incorporated into commercial products and generate its first revenues.
CEO at AlphanososCovid-19 Innovation Challenges by Innoget posted this:
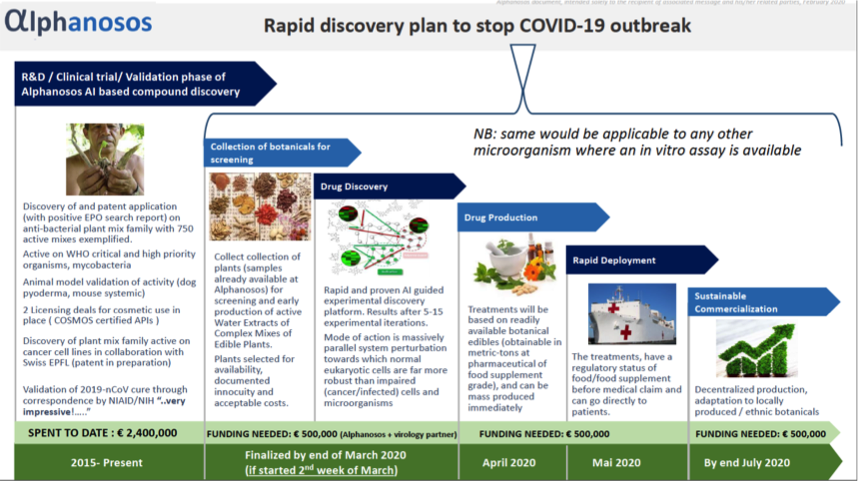
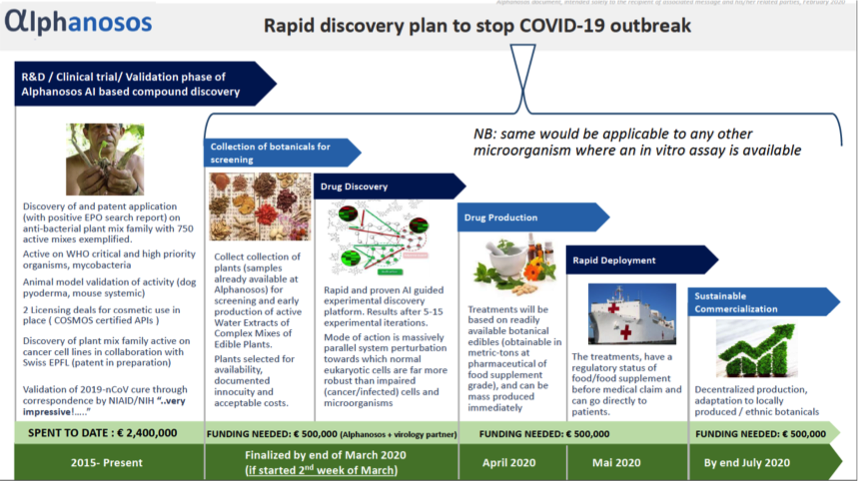
Alphanosos rapid discovery technology against COVID 19Alphanosos’ AI guided rapid discovery technology, validated in antimicrobials and anticancer, is expected to develop within 3 weeks of experimental work with a virology partner an anti-COVID-19 treatment composed of a synergistic mix of extracts of edible plants, chosen for being available in large amounts and with good traceability. Such treatment is, therefore, and also thanks to the innovative elaboration process, immediately available to enter large curative clinical trials, to be followed by country-wide deployment in a matter of weeks, for curative and for preventive goals (because of safety which is guaranteed by the edible nature of the mix).Pascal Mayer posted this:
Alphanosos rapid discovery technology against COVID 19Alphanosos’ AI guided rapid discovery technology, validated in antimicrobials and anticancer, is expected to develop within 3 weeks of experimental work with a virology partner an anti-COVID-19 treatment composed of a synergistic mix of extracts of edible plants, chosen for being available in large amounts and with good traceability. Such treatment is, therefore, and also thanks to the innovative elaboration process, immediately available to enter large curative clinical trials, to be followed by country-wide deployment in a matter of weeks, for curative and for preventive goals (because of safety which is guaranteed by the edible nature of the mix).
CEO at AlphanososAllan M Olbur posted this:
Alternative source of fresh drinking water for Beverage Bottling PlantsThe water quality in specialty beverages plays a huge role in the finished product. Without a proper filtration process, you could be letting unwanted minerals and bacteria alter the taste and look of your drink.
Chairman at Green Technology Global, Inc.Universidad de Alcalá-OTRI posted this:
Altimeter based on radar, inertial and atmospheric pressure systems for aerial, acrobatic and unmanned vehicles.The Intelligent Systems Research Group of the University of Alcalá presents an altimeter based on radar, inertial and atmospheric pressure systems for aerial, acrobatic and unmanned vehicles. It is a sensor capable of measuring height with respect to the ground integrating radar, barometric and inertial technologies. The group seeks to achieve licensing, collaboration or commercial agreements with technical assistance, with companies or research groups related to the aeronautical and aerospace sector. Dirección de Transferencia Tecnológica (DIT) Universidad Adolfo IbáñezUniversidad Adolfo IbáñezDirección de Transferencia Tecnológica (DIT) Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez
Dirección de Transferencia Tecnológica (DIT) Universidad Adolfo IbáñezUniversidad Adolfo IbáñezDirección de Transferencia Tecnológica (DIT) Universidad Adolfo IbáñezAgente de Innovación at Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez
View ProfileDirección de Transferencia Tecnológica (DIT) Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez posted this:
Alzheimer Early Test, a machine learning method to preemptively detect Alzheimer desease.The software addresses the need to identify the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease in patients at an early stage of life, which can be crucial for implementing preventive interventions and more effective treatment, but above all for planning in advance the legacy that the affected person will leave to their family and loved ones, as well as for making the best decisions together for both parties. Using a machine learning algorithm trained with data from the GERO cohort, the software has the ability to predict the risk of a patient developing Alzheimer's disease at an early age. It is based on dimensionality reduction techniques to analyze a panel of microRNA data from the GERO cohort, which includes information on mental health, laboratory chemistry measurements, and other relevant variables. This approach allows the software to generate accurate and personalized predictions about the risk of Alzheimer's for each patient, which can guide clinical decisions and improve health outcomes.
Agente de Innovación at Universidad Adolfo IbáñezSayali Warad posted this:
An Algorithm solution for the computation of nonplanar continuous interweaving 3D Printing tool path for polymers and polymer composite materialAn implemented algorithmic solution for the generation of continuous interweaving algorithms toolpath for additive manufacturing of medium to large parts using stable polymer matrices
IP Market Analyst at University of Alberta, Technology Transfer ServicesTaeho Kim posted this:
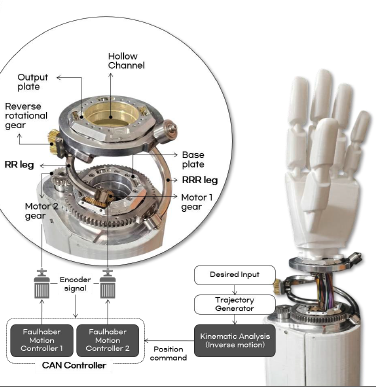
An Architecture-Level Wrist Platform Enabling Reliable and Scalable Robotic Manipulation in Contact-Rich Tasks.This technology is an architecture-level robotic wrist platform that addresses reliability limits caused by structural coupling in conventional wrist designs. By structurally decoupling range of motion, stiffness, and tendon routing through a parallel linkage with an intermediate plane, the platform achieves wide motion, high rigidity, and stable load handling without control compensation. A large hollow routing channel enables scalable wire and sensor integration independent of wrist orientation. The design provides consistent manipulability and prevents abrupt payload drops in contact-rich robotic manipulation.
Director, Technology Transfer & Venture Building at IBU Inc.Irene Uceda posted this:
An electrical stable electrochemical sensor device based on Electrolyte-gated field-effect transistor (EGFET)CSIC has developed an electrolyte-gated field-effect transistor (EGFET) with enhanced electrical stability. These new EGFETs operate in aqueous environment, and are stable for more than 12 hours under continuous operation, greatly surpassing current state-of-the-art EGFETs. The increased stability makes them suitable for real life applications. Industrial partners are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement. An offer for Patent Licensing
Employee at CSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones CientíficasUniversity of Alberta, Technology Transfer Services posted this:
An Enantioselective and Modular Platform for C4ʹ-Modified Nucleoside Analogue Synthesis- New chemical process to produce C4'-modified nucleoside analogues. - Potential application in developing antiviral and anticancer medications, as well as oligonucleotide-based therapeutic treatments. - Provides new opportunities in drug design.Taeho Kim posted this:
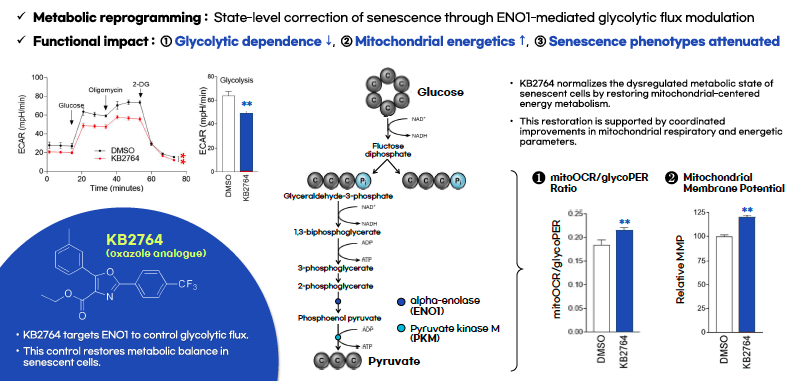
An ENO1-Targeting Oxazole Analogue Platform for Metabolic Rebalancing and Anti-Aging Applications.This technology provides a novel anti-aging approach by correcting cellular senescence through metabolic rebalancing rather than cell elimination. An ENO1-targeting oxazole analogue restores mitochondrial-centered energy metabolism and reduces glycolytic dependence in senescent cells. This state-level intervention attenuates key senescence phenotypes and supports functional rejuvenation. The platform offers a differentiated alternative to senolytic strategies with broad applicability across nutraceutical, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical development.
Director, Technology Transfer & Venture Building at IBU Inc.Universidad de Cádiz posted this:
An improved fast and high throughput method for the sequential measurement of nitrate and nitrite in water samplesWe have developed an improved fast and sequential protocol that permits the determination of low concentrations of nitrite and nitrate in aquatic samples using small volumes. It is ideal to analyse large sets of samples with different characteristics, since it is enough a small amount of water the volume and cost of reagents and consumables are reduced.Biomedical Research Center Sant Pau (IIB) posted this:
An in vitro methodology that offers the possibility to correct a genetic mutation through the use of advanced therapiesThe invention is an in vitro method that allows the recovery of F5 gene expression by the use of CRISPR/Cas9, a genetic modification tool of high precision. The access to exploit this methodology will benefit the licensee the possibility to perform cellular and genetic therapy to treat and reverse the disease.Peter Mogyorosi posted this:
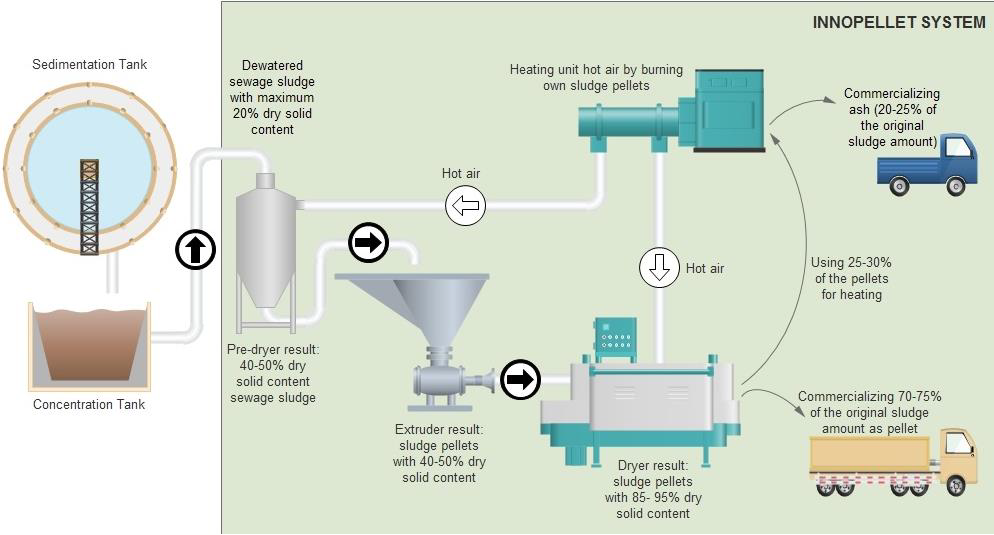
An Innovative Technology to Effectively Utilize and Recycle Sewage SludgeOur partner, a Hungarian company developed a patented technology that provides a solution for transforming municipal sewage sludge into solid fuel (Solid Recovered Fuel - SRF), which also enables sewage plants to achieve significant cost savings.
CEO at Laser Consult Ltd. Fabian BelinLuxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Fabian Belin
Fabian BelinLuxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Fabian BelinPartnerships Development & IP Valorization at Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)
Fabian Belin posted this:
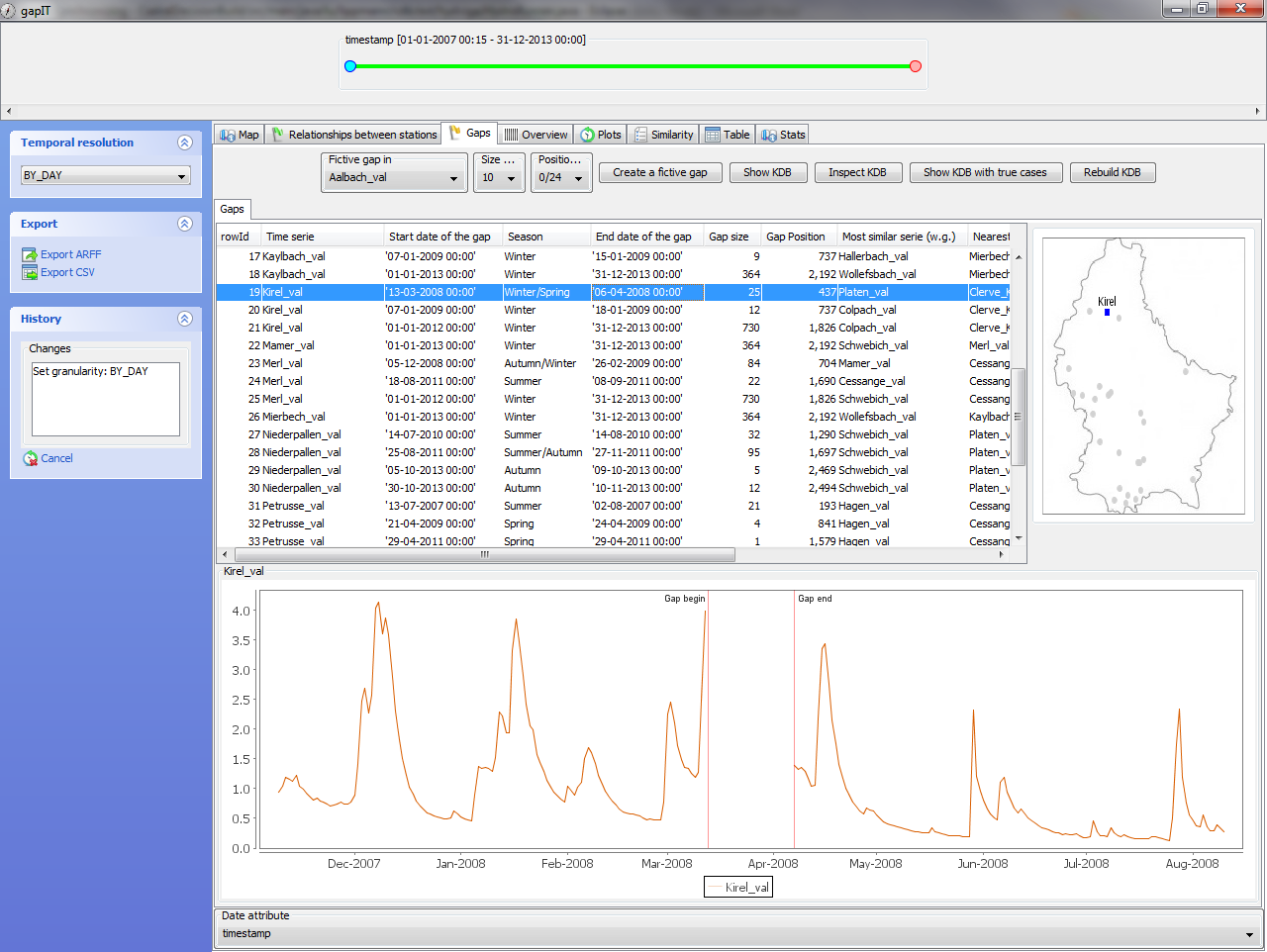
An interactive software tool to deal with missing values (gap filling) in hydrological time series for water managementgapIT is a JAVA-based software package that automatically calculates missing data using different data-infilling techniques, using hydrological discharge data series measures at gauging stations as input. Donor stations are automatically selected based on Dynamic Time Warping, geographical proximity and upstream/downstream relationships among stations. For each gap, the tool computes several flow estimates through various data-infilling techniques, including interpolation, multiple regression, regression trees and neural networks. The interactive visual application allows the user to select different donor station(s) than those automatically selected. The results are validated by randomly creating artificial gaps of different lengths and positions along the entire records. Using the Root Mean Squared Error and the Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient as performance measures, the method is evaluated based on a comparison with the actual measured discharge values.
Partnerships Development & IP Valorization at Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)Yeda posted this:
An Off-Line Image Search EngineAlthough images search engines are available online, offline networks and databases (in governmental offices, banks, etc.) require an efficient and reliable image search engine. Prof. Michal Irani and her team developed a method for Visual Inference of a collection of images, which builds upon collaboration between the images. This algorithm could implement inside offline networks without relying on external databases.SUSANA CÁMARA DECIMAVILLA posted this:
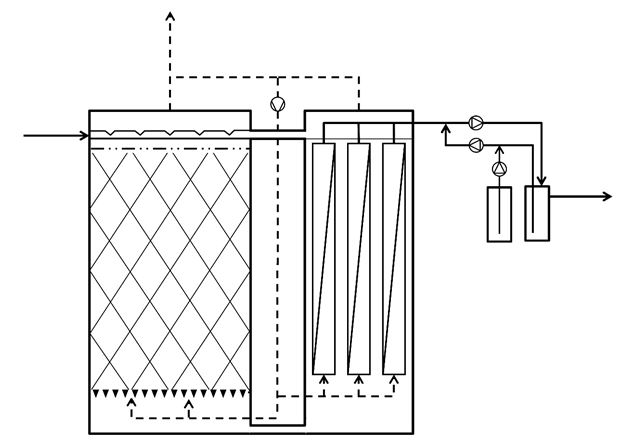
Anaerobic treatment of biodegradable waste liquidsBioreactor formed by two connected closed tanks (anaerobic digestion tank and filtration tank) for the anaerobic treatment of complex wastewater with biogas production. A support material is used, in a non-arranged way, increasing the active biomass accumulation capacity and allowing downwards flow in the digestion tank.
CEO at UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOSUniversidad de Alcalá-OTRI posted this:
Analysis and heuristic optimization software system for wind farm design.The utilization of technologies of soft computing has been vaguely applied to the optimization of the design of wind farms, and only with a limited set of parameters. Gheode group has developed a series of algorithms that consider in a much more realistic way the designing of parks, having in addition a great versatility to incorporate improvements or made-to-measure expansions for every client in particular.University of Waterloo posted this:
Anchor system for FRP platesFiber reinforced material and, in particular, fiber-reinforced-polymers (FRP), have been introduced for the structural rehabilitation and retrofitting of aging infrastructure as they are stronger than steel and not susceptible to corrosion. However, FRP plate can be more difficult to anchor to the base material (the underside of a bridge for example) because of low transverse compressive strength (i.e. it’s easily crushed), which can lead to breakage at or near the anchor point. Finding a suitable anchor system for FRP plates is a challenge as FRP plate is generally sensitive to lateral stress. It is, therefore, desirable to provide an improved anchoring system for fiber reinforced materials. Further, typical anchors for FRP plates tend to be very large, expensive, and difficult to manufacture.CSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
Andrographolide derivatives for its use as treatment for inflammatory diseasesAndrographolide derivatives for its use as treatment for inflammatory diseases related to cytokine storm. CSIC, the Polytechnic University of Valencia, the University of Navarra and the Medical Applied Research Foundation have developed semi-synthetic derivatives of andrographolide, a plant-derived product, very useful for the treatment of inflammatory diseases related to a massive cytokine release. These new compounds show a secure and specific way to control the inflammation, that can be caused by a viral infection, as COVID-19, a bacterial infection or by immunotherapy. Industrial partners are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement or codevelopment. An offer for Patent Licensing or Collaboration for developmentTTPU posted this:
Anti-adhesive Biopolymer CoatingResearchers have developed an anti-adhesive coating based on a polymer naturally and sustainable produced by a marine bacterium. This coating prevents the bacterial adhesion and the subsequent biofilm formation that usually leads to host bacterial infections difficult to eradicate and control with the antibiotics currently in use, namely in hospital environments. This coating can be applied in a cost effective way to a broad range of materials through the application of a universal glue.Leading Biology posted this:
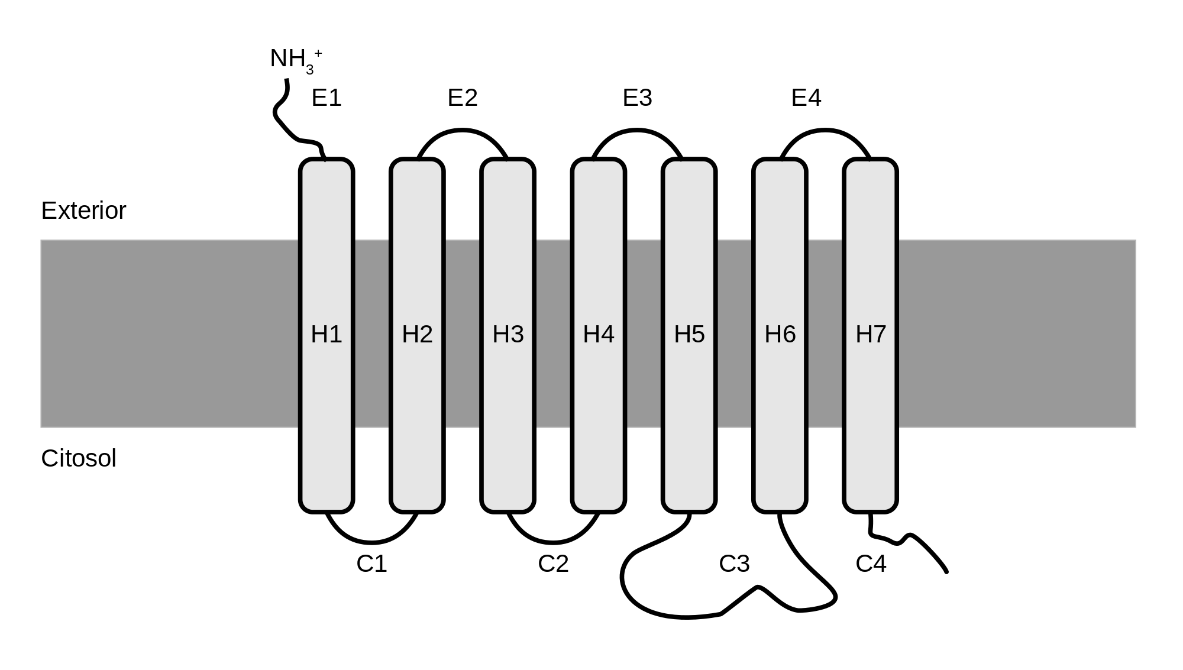
Anti-GPCR Antibody ProductionWith rich experience in antibody discovery and membrane protein studies, experts from Leading Biology have launched a membrane protein antibody development platform. We provide a one-stop service of anti-GPCR membrane protein antibody discovery service against a variety of GPCR targets now.
Business Development Manager at Leading Biology