Technology Offers Site map description
N
Incr-Edible Ingredients posted this:
New Improved Plant Protein Upcycled from Rice BrokensRE-Pro 80 UF is an ultra fine vegan, non-GMO, rice protein made from broken rice by enzymatic treatment. RE-Pro 80 offers: - high BV (biological value), - a strong amino acid profile comparable to animal protein - high NPU (net protein utilization). - plant-based protein source - a stable emulsion - clean label - meat-like texture - retain moisture over shelf life - interesting expansion features in extruded applications It is an 80% protein concentrate with good water uptake properties and a strong amino acid profile similar to that of animal proteins, without allergens. It works very well in combination with pea proteins and results in a palatable emulsion with a high protein content and a 1.0 PDCAAS.Javier Martínez González posted this:
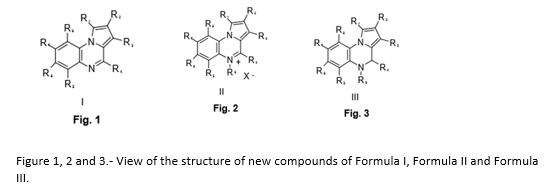
New inhibitor compounds of the tyrosine phosphatase 1B proteinThe research group in "Biological Chemistry" of the University of Alcalá has developed new compounds inhibitors of the Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Protein, which are related to new Formulas I, II and III, with methods to prepare them, with the use of them as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and with the use of the intermediates that lead to that compounds to prepare an inhibitor of PTP1B comprised by that formulas. These compounds have application in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which it is known that PTP1B is involved in the pathogenesis, so they can be used for the treatment of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and ischemic diseases of large and small blood vessels, conditions that accompany type 2 diabetes and other disorders where insulin resistance is indicated. The group looks for companies in the health and pharmaceutical sector with the aim of reaching technical collaboration agreements, commercial agreements or patent licenses agreements.
Commercialization Specialist at Universidad de Alcalá-OTRIUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
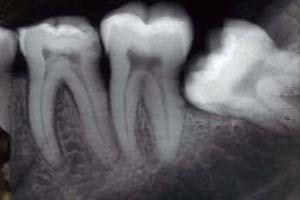
New inorganic cement for biomedical applicationsA novel magnesium phosphate cement with good properties for clinical applications has been patented and developed. It is envisaged as an excellent root canal filler for endodontic treatments, improving the commercial materials currently used for this application. Partners to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.SUSANA CÁMARA DECIMAVILLA posted this:
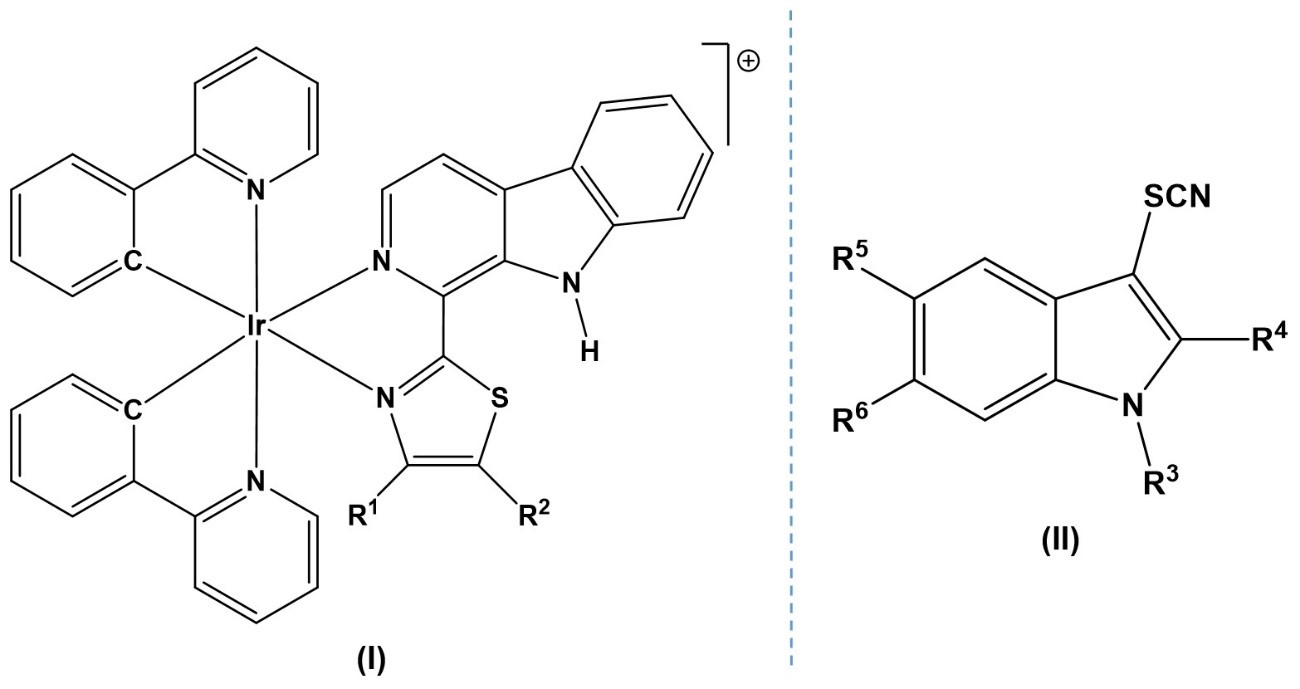
New iridium(III) complexes with application as photo-catalyst and for the treatment of cancerResearchers from the University of Burgos have patented a synthetic process of cationic Iridium(III) complexes with formula (I). Moreover, they have developed a one-pot protocol for the regioselective synthesis of 3-thiocyanato indoles (II) from their corresponding indolines. On the other hand, the use of these Ir(III) complexes as potential therapeutic photosensitizers for antitumor photodynamic therapy is also protected.
CEO at UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOSUNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New light materials cement base with improved properties for construction and civil engineerA research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base are cement and have improved for the construction and civil engineering properties, especially for the use thereof as indoor / outdoor carpet, as landfill soil and grouting factories. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New light materials plaster base with improved properties for constructionA research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base is gypsum and construction have improved properties, especially for the use of the same mass as coatings or to prefabricated interior. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New lightweight lime based materials with improved properties for constructionA research group at the University of Burgos have patented different materials whose base is the lime and they have improved properties for construction, particularly for the use thereof as coatings used in Artistic Heritage. The feature common to all is that different wastes are used for which the criteria for their use and basic dosages to ensure strength and durability are set as well as a high degree of performance and application.Taras Maiula posted this:
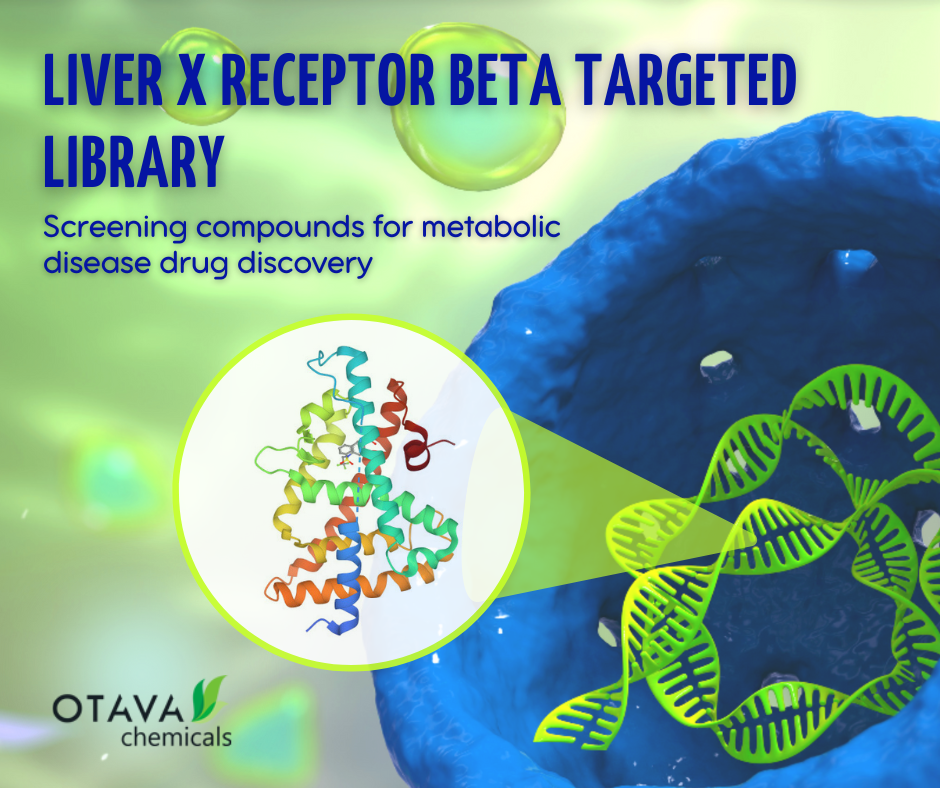
New Liver X receptor β Targeted LibraryOTAVA offers new Liver X receptor β Targeted Library which is targeted towards Liver X receptor β and comprises 436 small screening compounds.
Head of the QC department at Otava Research InstituteUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
New lossless data compression system with quick operation and high compression efficiencyA joint UB/UPC team has developed a new lossless data compression system excellent for applications requiring at the same time high compression ratios and quick operation with low CPU load. The system under the named FAPEC (Fully Adaptive Prediction Error Coder) is an algorithm that combines low processing requirements with high compression efficiency under almost any scenario. Partners to further develop the system and/or to establish license agreements with technical cooperation are sought.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New low cost colorimetric sensors, both solid and in aqueous solution, for the naked eye detection in situ and quantification of nitro-explosives (TNT)It is known the high toxicity of nitro-explosives, namely TNT, which are easily absorbed by the skin and the intestinal tract. It is also known the presence of this compound in contaminated civil areas arisen from older military installations, or even from terrorist attacks. This causes both health and environmental problems. In order to meet this need we have developed new colorimetric, simple, rapid and cheap colorimetric sensor for the in situ detection of trace amounts of TNT by non-specialized personnel and by conventional techniques sensors (replacing the commonly known IMS, GC, HPLC).Amnon Michael Cohen posted this:
New Maritime Discovery innovated into special rewarding opportunityThis yet new original discovery which has been innovated for granting few special advanced performance and maneuvering abilities, improved safety and economic plus superior comfort capabilities, representing the most advanced simplified technology you can add to any and all boats vessels and ships at low cost. There are more than 10 commercial benefits which are safe as tested and identified. Wisdom is indicating to us that we are better to find the suitable major corporation who will welcome the opportunity to be partner from the start, as if it is an in-house innovation they were not able to develop or discover as the inventor has, and be the ones to bring the technology and tap the vast market projected for the project – when you see the many commercial benefits and global spectrum of the “Power-fins” product line or the “Superior Hulls Design” itself.
InventorCSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
New material based on manganese oxide with gas generation and high temperature regeneration capacityCSIC has developed a material based on a mixture of metal oxides. This new material is capable of releasing oxygen gas during its reduction through an endothermic process and regenerating in air at high temperature (800-1000 ºC) releasing energy. The material behaves in a stable manner in successive reduction-oxidation cycles and has improved properties with respect to other similar materials available for processes in this type of chemical loops. Companies interested in patent licensing are sought for the development and use of materials capable of releasing oxygen gas. An offer for Patent LicensingJavier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
New metal-free electrocatalysts for fuel cellsThe Carbon Materials and Environment Research Group of the University of Alicante has developed a new method for obtaining carbon materials with excellent properties such as electrocatalysts in fuel cells or metal-air batteries. The process is based on the thermal treatment of polyaniline (or its derivatives) at high temperature and allows to obtain metal-free carbon materials with a high performance, in a very simple, fast way and in a single stage. These novel materials are characterized by their excellent catalytic activity and selectivity in the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline medium, they are very stable and resistant to methanol and carbon monoxide poisoning, and above all, they stand out for their low manufacturing cost, which makes them promising candidates to replace the current commercial platinum-based catalysts. We are looking for companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation.
Universidad de AlicanteUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
New method for controlled synthesis of mesoporous solids from any kind of POM based saltMesoporous solids are compounds used as catalysts and also as catalysts support in many chemical reactions. Catalysts are chemical compounds that increase speed reaction without modifying its own chemical characteristics. Same of them are used in the same phase that reagents and they are called homogeneous catalysts. Other are supported or imbedded in a porous surface, so called heterogeneous or contact catalysts. Most of the catalysts are extremely environmentally dangerous, as they are based in H2SO4 and HF, or very expensive, as they include noble metal compounds. In order to solve it, intense research in the latest decades has come up with catalysts based on polyoxometalates (POM). POM are a large family of nanoscale metal-oxide anionic clusters that combine easily with external positive ions to achieve electroneutrality. Regarding catalysis, POM group based on Keggin molecular structure is the most interesting because it confers them acid properties and great solubility in watery solutions. In that case, positive ions are protons and compound is called heteropolyacid (HPA). It has applications as homogeneous catalysts. POM can also be used as heterogeneous catalysts when replacing positive ions by cations to obtain the corresponding insoluble salt: the cation combined with the POM determines degree of solubility, thermal stability, acidity and porosity of the salt. These catalysts must provide a great superficial area, i.e. a great number and size of porous to provide a big number of loci to adsorb catalysed reactions. Nowadays, according to the cation used (ammonium, caesium) specific surface of about 100 m2/g (microporosity) may be achieved, but mesoporosity does not appear or it happens under no control. The research group has developed a method to obtain mesoporous solids from any kind of POM based salt. Method is quite simple and synthesis reaction, according to the cation used, is controlled by temperature and pH.Jagiellonian University posted this:
New method for efficient differentiation of human adipose tissue MSCs into bone cellsThe invention opens up the possibility of efficiently homing adipose tissue MSCs to differentiate into bone cells in vitro. The subject of the invention is a method for rapid and efficient differentiation of adipose tissue MSC cells into bone cells under laboratory conditions. The method was achieved by a) developing compositions of culture media for MSCs of adipose tissue, b) using so-called basic or modified bioactive growth surfaces for MSCs of adipose tissue and c) using so-called "dynamic" culture conditions for MSCs of adipose tissue.University of Huelva posted this:
New method for manufacturing magnetic cores by powder metallurgyMagnetic cores in amorphous state are usually produced by placing together very thin amorphous ribbons from a material obtained by the melt-spinning technique. The new patented method produces the amorphous material by mechanical alloying, a traditional process in the powder metallurgy field. This technique allows a higher control on the amorphisation process and the properties of the amorphous obtained powders. These powders are then consolidated by the very quick process known as Electrical Resistance Sintering (also Electrical Discharge Consolidation/Sintering can be used). A final amorphous material, without the typical frontier between ribbons of melt spinned materials, which clearly affect properties, is obtained.University of Huelva posted this:
New method for manufacturing powder metallurgy magnetsThe conventional method of press followed by furnace sintering is now substituted by an electrical consolidation method. This allows joining in a single step the previous pressing/sintering processes, and, due to the promptness of the process, the use of controlled atmospheres is not necessary. The steps of magnetization, and eventual thermal treatments, can be carried out in the same container, without being necessary to manipulate the product.OTRI-Universidad de Málaga posted this:
New method for prognosis of breast cancer recurrenceThe invention relates to the field of oncology and cancer treatment and prognosis. The invention includes methods for predicting the risk of recurrence of breast tumors using the expression signature of particular miRNAs.
Technology Transfer Office (TTO) at Universidad de MálagaUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
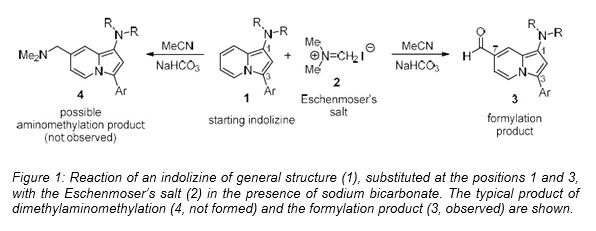
New method for rapid, simple and efficient detection of nitritesThe Institute for Organic Synthesis (ISO) has developed a new method for the formation of indolizines, based on the use of the Eschenmoser salt, the products of which allow the rapid, simple and efficient detection of nitrites in water or food. This invention solves the disadvantages of the methods known so far, since they do not require highly-reactive and/or highly-toxic substances. It can be applied both in solution and on cotton swabs. The group is looking for companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation.IMIM Institut Recerca Hospital del Mar posted this:
New method for the determination of the risk of atypical fractures in patients treated with bone remodelling inhibitors.Up to date there is not any technology for detecting the risk to suffer atypical fractures related to long-term treatment with bone remodelling inhibitors. The invention will be of usefulness for individualize treatments in patients treated with bone remodelling inhibitors by detecting the individual risk of suffering atypical fractures. The invention is planned to be included into an in-vitro diagnostic tool for the atypical fracture, which will be included into standard disease management protocols and therefore used routinely by physicians prior to and after the prescription of bone remodelling drugs and further osteoporosis drugs. Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease with a characteristic decrease in bone mass and density which can lead to an increased risk of fracture. There are two types of osteoporosis: •Type 1: most common in women after menopause, named postmenopausal osteoporosis •Type 2: Senile osteoporosis, occurs mostly after age of 75 years and has equally effect in women and in men Based on the WHO diagnostic criteria, approximately 22 million women and 5.5 million men aged between 50 and 84 years had osteoporosis in the European Union (EU) in 2010, whilst osteoporosis can be found in the list of 10 most important diseases named by the WHO. Due to changes in population demography, the number of men and women with osteoporosis might rise from 27.5 million in 2010 to 33.9 million in 2025, corresponding to an increase of 23%. The number of new fractures in the EU in 2010 was estimated at 3,5 million cases, in between these approximately 620.000 hip fractures, 520.000 vertebral fractures, 560.000 forearm fractures and 1.800.000 fractures of i.e. pelvis, rib, humerus, tibia, fibula, clavicle, scapula, sternum, and other femoral fractures. Two thirds of all fractures occurred in women. In 2010, the number of deaths causally related to fractures was estimated at 43.000. The corresponding cost of osteoporosis in the EU, also in 2010 figures, including pharmacological intervention, was estimated at €37 billion out of which costs of treating fractures represented 66%, pharmacological prevention 5% and long term fracture care 29%. The total health burden was estimated at 1 180 000 lost Quality Adjusted Life Years (QALY) for the EU. The total cost in the EU might rise from €98 billion in 2010 to €120 billion Euro in 2025. The use of osteoporosis drugs has increased considerably. Approved pharmacological interventions (bisphosphonates, strontium ranelate, raloxifene, denosumab and parathyroid hormone peptides) are widely available but their use is restricted by reimbursement policies. Alendronate (a bisphosphonate) is the most commonly prescribed agent, accounting for approximately a quarter of the total value of sales. The potential users/partners are pharmaceutical companies, excluding pure generic companies (lacking development resources, relevant lobbying and sales channel to the policy makers and practitioner) selling drugs in the indication osteoporosisUniversitat de València posted this:
New method for the production of metallic oxides with spinel structureThis procedure is faster, with lower energy consumption and generates purer spinels than known methods for spinel production. With this invention, it’s possible to provide new methods for obtaining spinels or other mixed oxides with a higher processability and versatility than those existing to date, allowing also for obtaining new spinels and removing the need for extremely costly phases in time or energy, including milling or heating at temperatures up to 1200ºC.Universitat de València posted this:
New method for the synthesis of inert metallic nanoparticlesThe most remarkable advantages provided by this technology are: • Rapidity of the metallic nanoparticle synthetic method, as it consists of only one step. • Efficiency, since size, shape and concentration of nanoparticles are controlled, as well as, their production in organic or inorganic soluble solution. • Reduced production costs, as high temperatures are required by other alternative laser ablation methods.Universidad de Alcalá-OTRI posted this:
New method of transmission and estimation of the arrival time of acoustic signals for localization systemsThe Research Group of Electronic Engineering Applied to Intelligent Spaces and Transportation (GEINTRA) of Alcalá University has developed a procedure to estimate the arrival instant of acoustic signals for localization systems based on a non-coherent and capable DFT-S-DMT * modulation to compensate the Doppler effect, for its application in acoustic localization systems. GEINTRA seeks companies from the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) sector to sign technical cooperation agreements, commercial agreements with technical assistance and patent licensing agreements. * Discrete multi-tone modulation, widening by discrete Fourier transformUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
New method to detect spacer acquisition in CRISPR structuresInsertion of new CRISPR spacer units is very infrequent in most species. Detection of these events usually requires large screenings of CRISPR clusters of a high number of clones. In order to decrease the number of clones to be tested, it is possible to select adapted cells when such acquisition changes the immunity pattern (i.e. enables for the degradation of target molecules). This causes a bias against detection of insertions of other sequences and cannot be executed in cells with silenced CRISPR immunity. In this sense, the availability of a selectable tool for readily detecting spacer insertion independently of its consequences over the degradation of target genetic elements is highly advantageous compared to the methods currently in use. CNIC (TTO)Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)CNIC (TTO)
CNIC (TTO)Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)CNIC (TTO)Technology Transfer Office at Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)
View ProfileCNIC (TTO) posted this:
New method to improve treatment of atrial fibrillationResearchers from the CNIC and HCSC have developed a system to guide ablation procedures in a patient-specific way in complex cases of persistent atrial fibrillation, identifying these key regions to be treated with great precision and specificity. Furthermore, it does not require additional equipment or consumables, but only software that could be implemented within any conventional electroanatomical browser, so it would not make current pulmonary vein isolation procedures more expensive, with the advantage of being able to perform patient-specific ablation in complex cases.
Technology Transfer Office at Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)Universitat de Lleida posted this:
New method to increase yolk color and egg nutritional qualityThe University of Lleida seeks industrial partners with expertise in the sector of crop production to adopt a new technology of optimized feed solution for egg producers (poultry market). The type of partner sought is for the regulatory codevelopment and commercialization of our solution under a technology license agreement.Universidad de Alicante posted this:
New method to quantify the self-repair of polymeric materialsThe Adhesion and Adhesives Laboratory of the University of Alicante has developed a new method (equipment and process) to determine the degree of self-repair and to monitor the kinetics of self-repair of polymeric materials. The new method also makes it possible to follow the self-repair process of composites, ceramic materials, materials based on cement, mortar or concrete, and textile materials.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
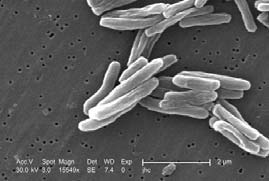
New method to test tuberculosis virulenceA new easy, fast and reliable method to determine the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) has been developed by a group of scientists from UPC and IGTP. Partners to further develop the technology and/or to establish comercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New methodology for the catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds environmental friendlyThe invention relates to a new general method for the reduction of nitroarenes to anilines using a Mo(VI) catalyst and pinacol as reducing agent. The products obtained show excellent yields. It should be noted that this new method uses an easily available and non-toxic reducing agent that generates non-toxic byproducts which are easily separated from the amine synthesized.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New methods for the detection and discrimination of contaminants and organic metabolites of high environmental impact by means of fluorogenic probesThe research group develops new selective fluorogenic probes for organic molecules of low molecular weight and high social and environmental impact. The newly developed fluorogenic probes are able of show large differences of fluorescence in the presence of certain analytes and they are oriented to the resolution of detection problems for contaminants of high environmental impact for which a satisfactory solution does not exist, such as phosphorylating reagents from chemical weapons, methylmercury, cyanide ion, doping substances and recreational abuse drugs. By incorporation of the fluorogenic probes to silica nanomaterials, the research group generates new luminescent sensory materials of toxicological and environmental utility.