Technology Offers Site map description
M
University of Alberta, Technology Transfer Services posted this:
Methods of Efficient Lignin Conversion● Methods for processing Kraft lignin into monomers or alternative liquid fuels. ● Facilitates sustainable production of bio-oil with a high yield under moderate conditions.Meghan Meyer posted this:
Methods of Identifying Novel Proteins and Antigens in Cancer Cells- Novel method to identify tumor-specific antigens for cancer immunotherapy. - Single-Molecule Real-Time (SMRT) Full-Length RNA-Sequencing to identify neoantigens or potential neoantigens as predictive biomarkers and synergistic treatment targets for cancer immunotherapy. - Method uncovers antigens that would be missed by typical short-read RNA sequencing.
Other at Georgetown UniversityGeorgetown University posted this:
Methods of Treating Gastrointestinal Cancers and Tumors Thereof Using Combination Therapy- Enhances sensitivity of gastrointestinal tumor cells to oxaliplatin, improving treatment outcomes. - Targeted therapy for patients with HR-DDR mutations and/or a family history of breast or ovarian cancer syndrome. - Inhibits tumor growth, reduces size, and prevents metastasis of gastrointestinal cancersAlex Michine posted this:
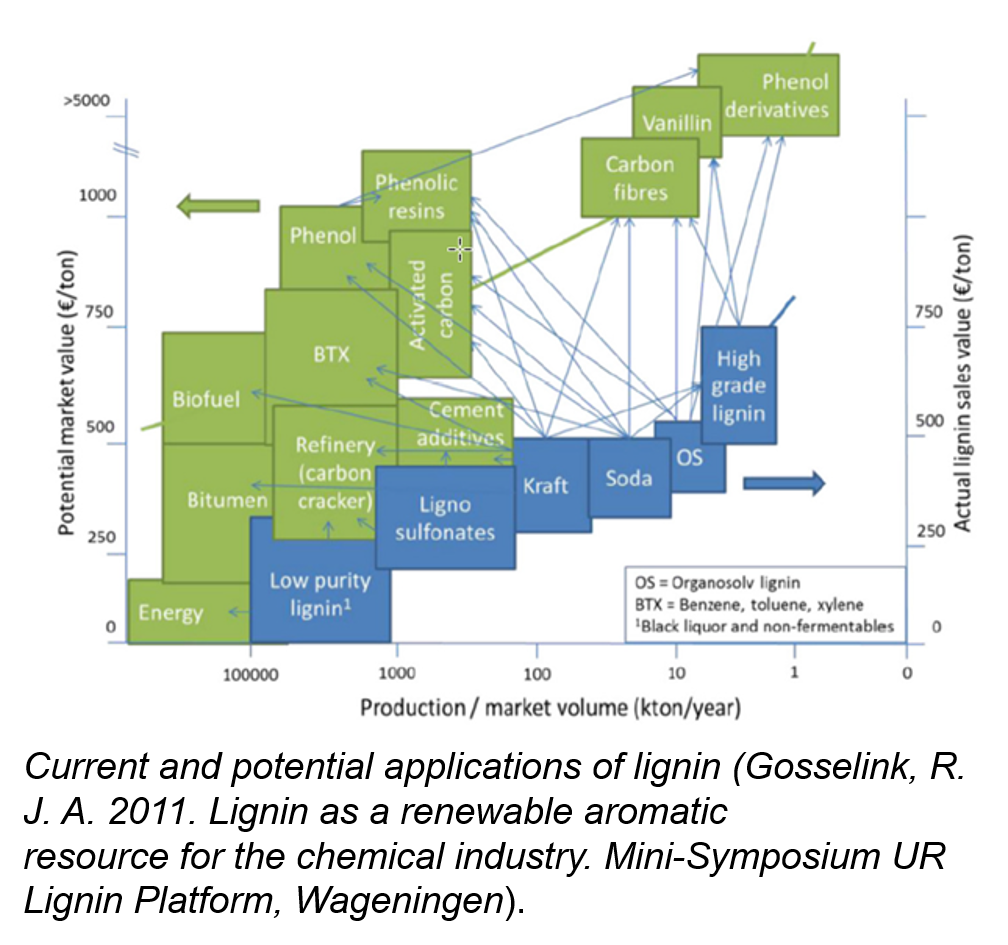
METNIN™ TECHNOLOGY IS A LIGNIN REFINERY - SUSTAINABLE PATH TO REPLACE OLD BASED CHEMISTRY IN HIGH VALUE END USER PRODUCTSMETNIN™ Technology is developed to refine lignin to end-user specific characteristics. Our technology is agnostic to lignin source and provides the missing link in the value-chain between crude lignin and high value lignin fractions for specific end user products. Metnin™ is enabling lignin valorisation towards wide range of drop-in sustainable solutions in e.g. coatings, resins, plasticizers, polyurethanes, and moisture/humidity resistance packaging. MetGen’s technology has been proven in multiple pre-commercial installations and enables cost-efficient conversion of lignin into cascade of intermediate building blocks of specific molecular size.Basic engineering package, CAPEX and OPEX estimate available.
CEO at MetGenCSIR posted this:
Micro-Enterprise Media Engine (MEME)The CSIR has developed a solution to deliver unbroken video streams over mobile networks from 2.5G (rural) – 4G (Wi-Fi) at data costs ranging from as low as R2 up to R50 per viewing hour. Live streaming to mobile devices in rural and some peri-urban communities is problematic as buffering severely impacts the experience. Streaming at ultra-low data costs remains a challenge. In addition, the commercial television industry is dominated by large regional monopolies that own expensive delivery mechanisms, with few opportunities to create a new generation of small, medium and micro enterprises (SMMEs) global broadcasters. The CSIR-developed Micro-Enterprise Media Engine (MEME) enables a broadcast manager to commission work from content creators, and to then upload, schedule and broadcast to audiences, while also connecting audiences to advertisers. “The solution has a low barrier to entry, and it is packaged into an offering as ‘broadcasting in a box’, suitable to enable media start-ups to become global broadcasters,” says CSIR chief engineer, Keith Ferguson. The technology is well suited to closed-group broadcasting with social media interaction as the feedback mechanism. Closed groups would typically include corporate marketing, communications and training of a dispersed workforce, distance learning for universities or schools with students in low-income groups, community broadcasting in mining communities and others. The MEME platform can benefit the information and communications technology corporate sector to host and develop applications that are customisable for the many market applications of this technology. “Of special interest is the inclusion of start-ups and SMMEs in partnership with the corporate sector,” says Ferguson.CSIR posted this:
Micro-Enterprise Media Engine (MEME)The CSIR has developed a solution to deliver unbroken video streams over mobile networks from 2.5G (rural) – 4G (Wi-Fi) at data costs ranging from as low as R2 up to R50 per viewing hour. Live streaming to mobile devices in rural and some peri-urban communities is problematic as buffering severely impacts the experience. Streaming at ultra-low data costs remains a challenge. In addition, the commercial television industry is dominated by large regional monopolies that own expensive delivery mechanisms, with few opportunities to create a new generation of small, medium and micro enterprises (SMMEs) global broadcasters. The CSIR-developed Micro-Enterprise Media Engine (MEME) enables a broadcast manager to commission work from content creators, and to then upload, schedule and broadcast to audiences, while also connecting audiences to advertisers. “The solution has a low barrier to entry, and it is packaged into an offering as ‘broadcasting in a box’, suitable to enable media start-ups to become global broadcasters,” says CSIR chief engineer, Keith Ferguson. The technology is well suited to closed-group broadcasting with social media interaction as the feedback mechanism. Closed groups would typically include corporate marketing, communications and training of a dispersed workforce, distance learning for universities or schools with students in low-income groups, community broadcasting in mining communities and others. The MEME platform can benefit the information and communications technology corporate sector to host and develop applications that are customisable for the many market applications of this technology. “Of special interest is the inclusion of start-ups and SMMEs in partnership with the corporate sector,” says Ferguson.IMDEA Energy posted this:
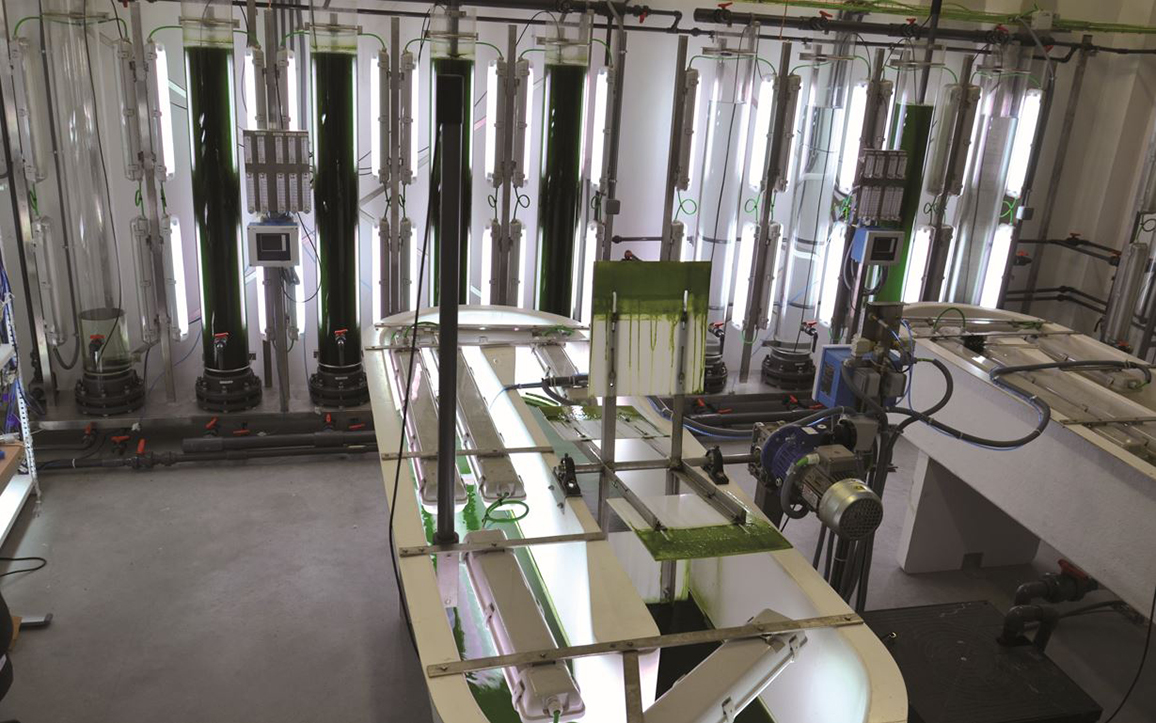
Microalgae cultivation in a versatile pilot plantIMDEA Energy has a modern pilot plant to conduct photosynthetic microorganism cultivation in photobioreactors, This plant allows optimization and scaling up the microalgae/cyanobacteria/bacteria culture from laboratory to pilot plant scale. The process parameters automation and the on-line control through an advanced software provide high versatility and flexibility to the pilot plant operation. The scientific expertise related to bioprocess development and optimization, along with high-quality facilities, make this pilot plant especially attractive for research cooperation agreements while it is also offered the technical assistance to other partners that need to scale photosynthetic based technologies. Proof thereof is the number of national and international projects that have been developed using this facility and applying the know-how of the researchers.Microbialtec Division posted this:
Microbial DNA Sequencing-Microbialtec ResearchMicrobial DNA sequencing technology is a rapidly developing research field in recent years. Researchers extract samples of microbial populations in the environment and analyze the genomes of microbes through DNA sequence analysis tools.jaume mir posted this:
Microbial extracts from saline marshes with outstanding moisturizing, UV-filter, wounding care and metal chelant propertiesSaline marshes are natural environments with hard conditions supporting life due to the high concentration of salts. Thus, microbial flora surviving there needs to develop high performance molecular mechanisms to retain water against osmotic pressure. Biochemize has developed a low-cost and non-invasive process for the isolation of those microorganisms and to obtain from those biomass extracts (containing high amounts of carotenes, licopenes and flavonoids, among other) with high capacities for the retention of water (much higher that those from hyaluronic acid), for filtering UV-radiation, for wounding care, and with outstanding properties as anti-oxidants and/or metal chelants. Applications for pharma, cosmetic and agrofood industries are proposed. A first set of studies of the properties of these extracts is available.
CEO at Biochemize SLCSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
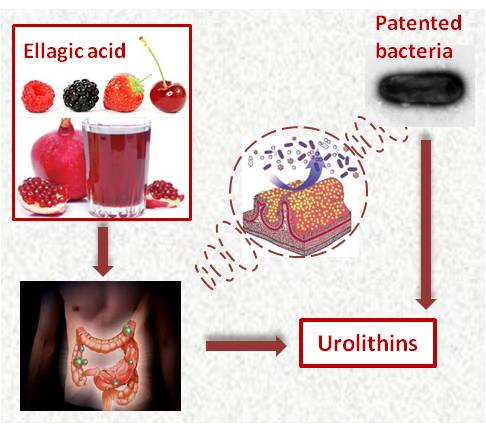
Microbial method for reproducing the human urolithin metabotypes in vitro and in vivoMicrobial method for reproducing the human urolithin metabotypes in vitro and in vivo CSIC has isolated and characterized from the intestine of a healthy woman a novel bacteria strain that produces urolithins and developed novel gut bacterial consortia comprising the mentioned novel bacterium and other bacteria wherein the consortia produce the mix of urolithins of metabotypes A or B, respectively, either in vitro or in vivo, including the newly characterized urolithin G. The microorganism, the novel urolithin, and the method for naturally producing all the human urolithins of both metabotypes are part of a patent application assigned to CSIC. Biotech companies and functional food or nutraceutical companies are sought for license and (or) development agreements. An offer for Patent LicensingKyoto University posted this:
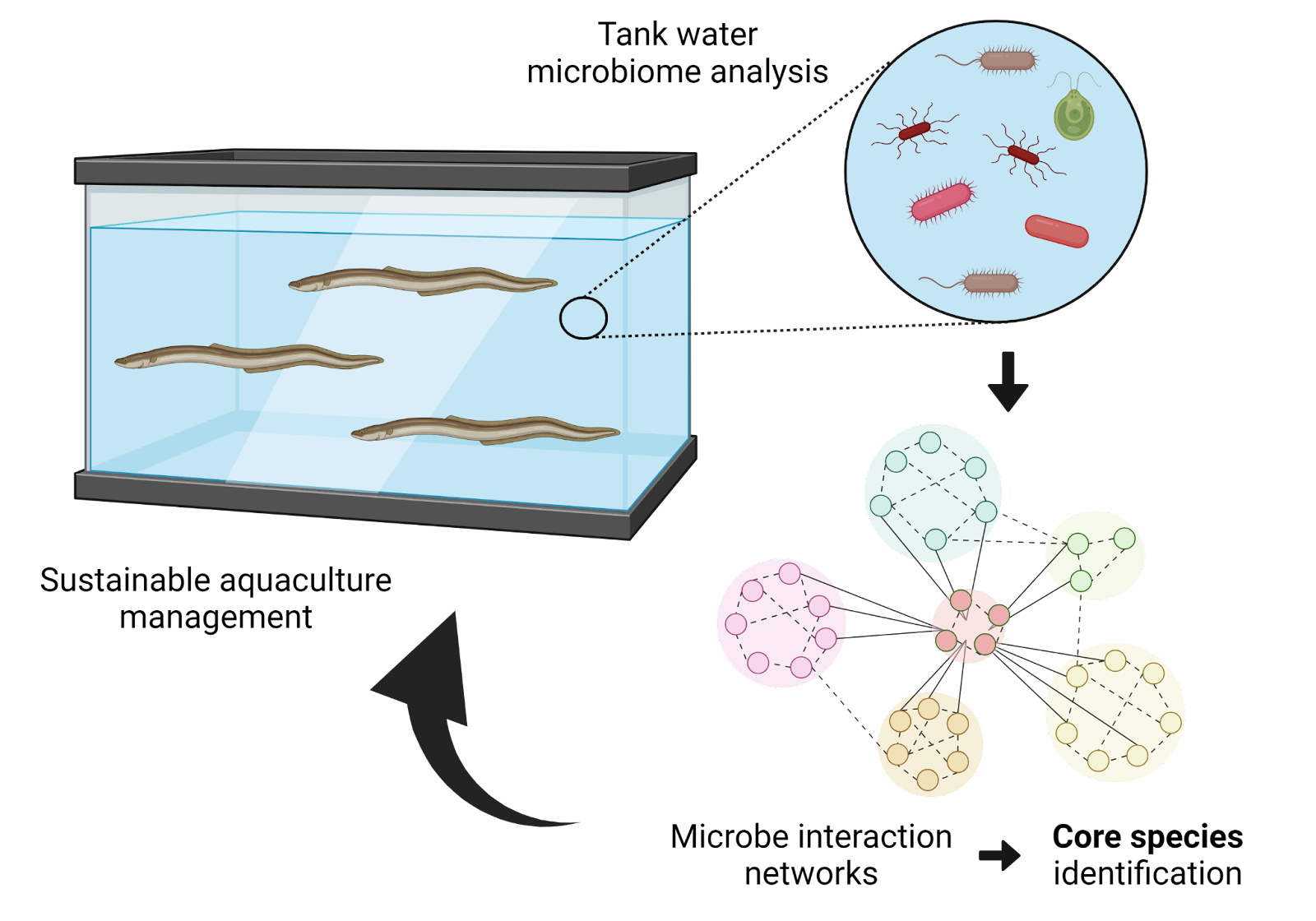
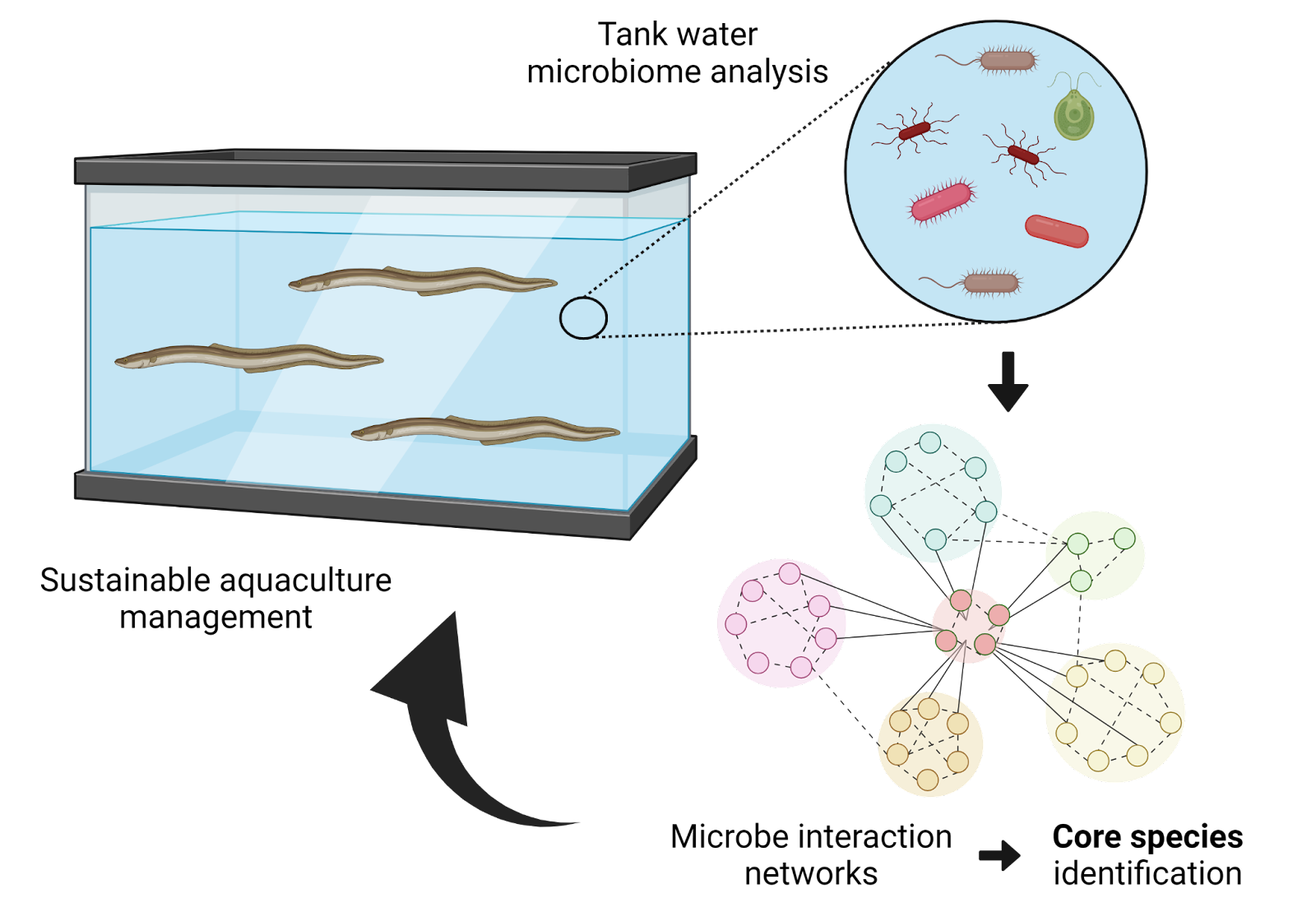
Microbial networks for sustainable aquacultureSeafood is a major source of nutrition for more than 1 billion people. Aquaculture has become an essential production method of seafood but is facing several challenges. Aquaculture contamination is a major limiting factor that impedes growth, reduces stocks, and requires additional costs for treatment and control of pathogens. Contamination control is particularly important in closed aquaculture systems on land. Conventional aquaculture management relies on drugs such as antibiotics and pesticides, and chemical sensors for nutrient monitoring. However, more sustainable options are actively being sought. Professor Toju and his team at Kyoto University developed a method of monitoring aquaculture microflora that provides useful information for optimizing seafood growth and preventing outbreaks of harmful bacteria. The technology has been tested in a recirculating aquaculture system of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) (Yajima et al. 2023).Larisa Sheloukhova posted this:
Microbial networks for sustainable aquacultureSeafood is a major source of nutrition for more than 1 billion people. Aquaculture has become an essential production method of seafood but is facing several challenges. Aquaculture contamination is a major limiting factor that impedes growth, reduces stocks, and requires additional costs for treatment and control of pathogens. Contamination control is particularly important in closed aquaculture systems on land. Conventional aquaculture management relies on drugs such as antibiotics and pesticides, and chemical sensors for nutrient monitoring. However, more sustainable options are actively being sought. Professor Toju and his team at Kyoto University developed a method of monitoring aquaculture microflora that provides useful information for optimizing seafood growth and preventing outbreaks of harmful bacteria. The technology has been tested in a recirculating aquaculture system of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) (Yajima et al. 2023).
Global Tech Commercialization at Kyoto UniversityLarisa Sheloukhova posted this:
Microbial networks for sustainable ecosystemsBackground Agroecosystems face multiple challenges worldwide. Agricultural lands are deteriorating, crops are exposed to extreme weather conditions, and new strains of pests resistant to chemical pesticides are emerging. In order to build sustainable agroecosystems, minimize devastating diseases, and maximize crop yield, understanding what drives ecosystem dynamics is of paramount importance so that the drivers can then be manipulated.
Global Tech Commercialization at Kyoto UniversityUniversidad de Alicante posted this:
MicroC@MPUS® . A Web-based educational environmentThe Innovation in Computer Science Unit at the University of Alicante has developed an e-learning tool called MicroC@MPUS®, a sophisticated World Wide Web-based educational environment that seeks to supply a virtual academic meeting space between teachers and students. Partners interested in acquiring the software rights are sought. University of Girona (OTRiT)Universitat de GironaUniversity of Girona (OTRiT)
University of Girona (OTRiT)Universitat de GironaUniversity of Girona (OTRiT)Technical Office for Research and Transfer at Universitat de Girona
View ProfileUniversity of Girona (OTRiT) posted this:
MICROconcentrator of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) in INdoor Environments (MICRO-IN)The accumulation of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in indoor spaces without adequate ventilation can exceed standard maximum thresholds by up to six times and trigger health problems. To address this, the LEQUIA research group proposes an efficient, low-cost and modular system, easily integrable with current systems, to be able to capture and concentrate this CO2, generating clean air along with a constant CO₂ stream of up to 95%.
Technical Office for Research and Transfer at Universitat de Girona University of Burgos (Spain)University of Burgos (Spain)University of Burgos (Spain)
University of Burgos (Spain)University of Burgos (Spain)University of Burgos (Spain)Small and Medium Enterprise
University of Burgos (Spain) posted this:
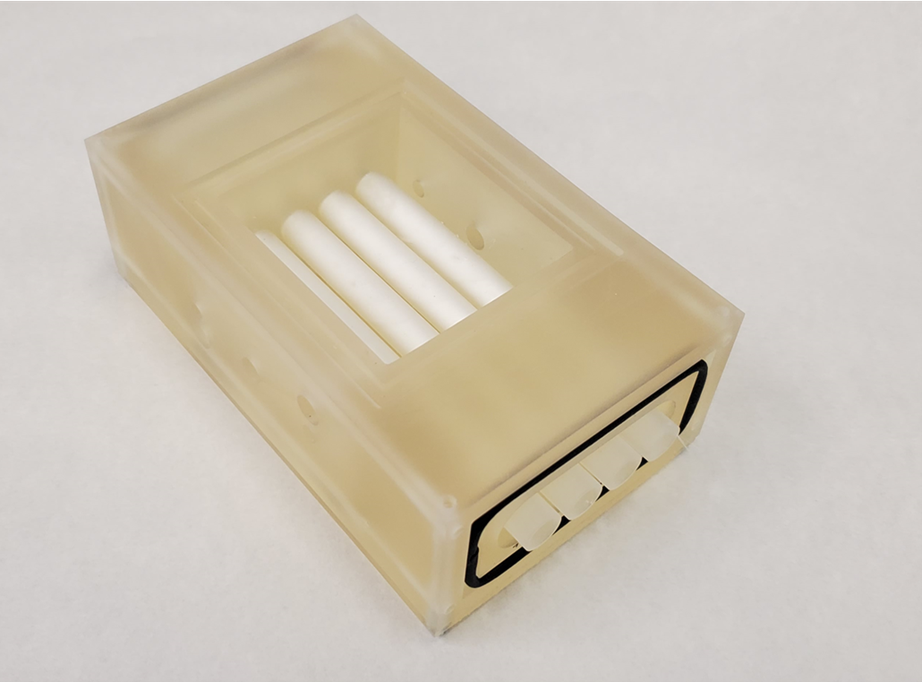
Microencapsulation of enzymes to accelerate cheese maturation processApplication of microencapsulation to control the function and action of the enzymes involved in cheese ripening and shorten processing times. The addition of encapsulated enzymes eliminates the problems associated with the direct addition (loss of enzyme in serum, bad distribution, reduced performance and quality alteration cheese) allowing a gradual and control action, reducing time maturation and therefore giving a quicker exit of the product to market.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
Microencapsulation of enzymes to accelerate the cheese ripening processResearchers at the University of Burgos are developing a technology of microencapsulation of proteolitic enzymes that reduces time cheese maturation process, maintaining their organoleptic characteristics.University of Waterloo posted this:
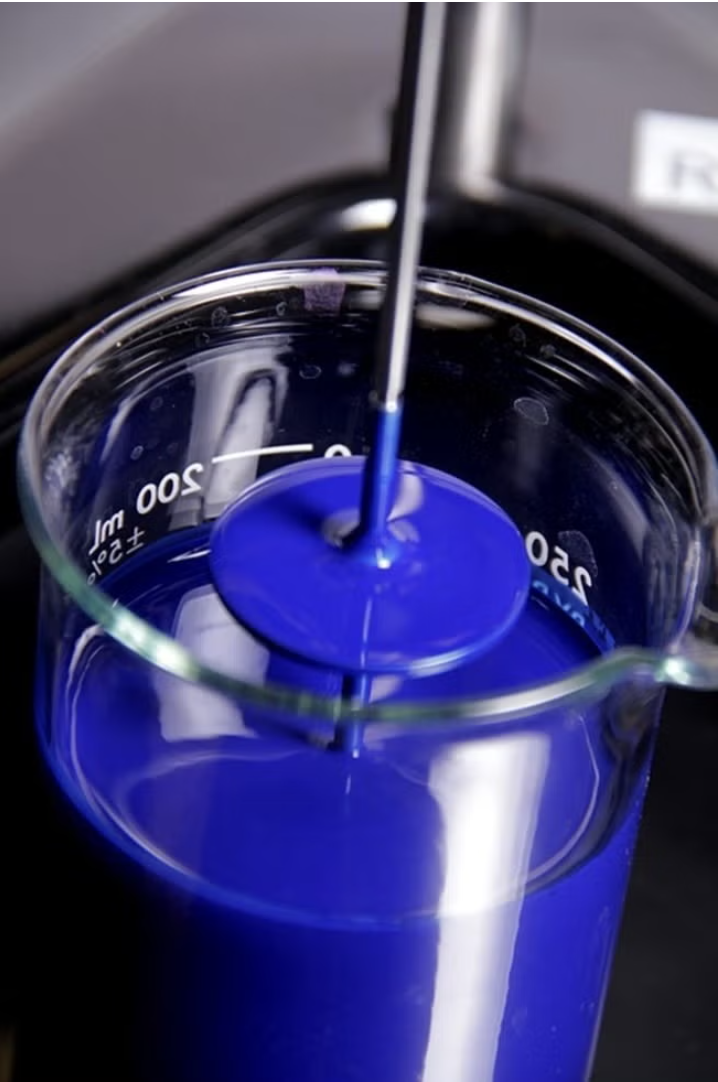
Microfluidic viscometer for the measurement of small-volume non-newtonian fluidsBackground The viscometer & rheometer market generated USD $683.0 million in 2017 and is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2017 to 2024. The viscometer market is valued at USD $483.0 million including different types of viscometers such as orifice, capillary, falling piston, rotational, falling ball, falling sphere, bubble, U-tube, inline, and vibrational viscometers. Inline process viscometer segment is expected to grow from USD$133 million in 2015 to USD $225 million in 2023 at 6.5% CAGR. The demand from petroleum, food, life science research and pharmaceutical industries is driving the market growth. For instance, the protein therapeutic market’s rapid growth has increased the demand for viscometers due to syringe-ability and because it is a relevant parameter for purification, fill/finish, and drug delivery. As viscosity is a key deciding factor in many diverse domains, there is a need for a device that can measure and analyze the viscosity with high precision and accuracy while requiring less sample volume (i.e., a few microliters).CSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
Microfluidics device for SERSThe CSIC has developed a microfluidic device for the performance of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) using a solid SERS substrate. By coupling this device to a Raman microscope, it is possible to detect very low concentrations of analyte in the flux directly in the microfluidic channel. Scientific instrumentation companies interested in licensing the patent for the development of accessories for Raman microscopy are sought. An offer for Patent LicensingUniversity of Waterloo posted this:
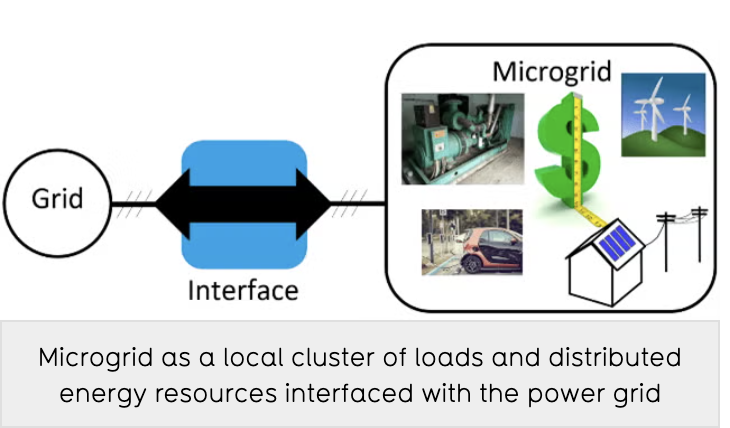
Microgrid Connector Controller (MGC): an effective controllable grid interface for microgridsBackground As renewable (and usually distributed) energy sources are taking a strong foothold in the market, the interest in the integration of distributed power generation and microgrids into power grids has significantly increased. A microgrid can be a cluster of load/power generator units such as an industrial complex or an Electric Vehicle (EV)/public transportation depot and renewable energy power sources such as wind farms and solar PV. Connecting microgrids to power grids is important as the electric power must flow between the two to assure continuous, safe, and economic supply of electric energy to all loads/consumers. Existing solutions for connecting microgrids to grids, including Back-to-Back (B2B) interfaces, are bulky and costly with limitations on frequency control.University of Waterloo posted this:
MicroLED on flexible substrateBackground While MicroLEDs have superior display properties when compared to LCD or OLED, the cost to implement the display media onto the backplane is very expensive and hence their applications has been limited to use in small screen size displays (i.e. smart phones).Universitat de València posted this:
Micromechanical dry exfoliation deviceThe main advantages provided by the invention are: Versatility: the method is applicable to any layered material and on any type of substrate. Simplicity: the method consists in a dry exfoliation without adhesive materials. Quality and reproducibility: the exfoliation is clean (no trace of adhesive), reproducible and it does not produce defects in the substrate. Efficiency: it is possible to deposit a high density of atomically thin layers of the material. Control: it is possible to control the pressure exerted, allowing for a fine-tuning of the deposition conditions depending on the nature of the layered material manipulated.Universidad de Alicante posted this:
Microneedle biosensor and remote monitoring system for hormone treatmentResearchers from the University of Alicante and the Technische Universität Dresden have developed a biosensor and an intelligent remote monitoring system that provides accurate, real-time information on hormone levels to patients and professionals. In addition, these data, through automatic processing techniques such as Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning, provide patterns for better treatment of these pathologies.CSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas posted this:
Microorganism and method to produce urolithinsProfessor Francisco Tomas group at CEBAS-CSIC has isolated and characterized the first urolithins- producing microorganism from ellagic acid and ellagitannins present in the diet. A urolithin producing method based on the use of the mentioned microorganism has been developed and both, the microorganism and the method are part of a Spanish priority patent application assigned to CSIC. Biotech companies, functional food or nutraceutical companies are sought for license and/or development agreements. An offer for Patent LicensingUniversidad de Granada posted this:
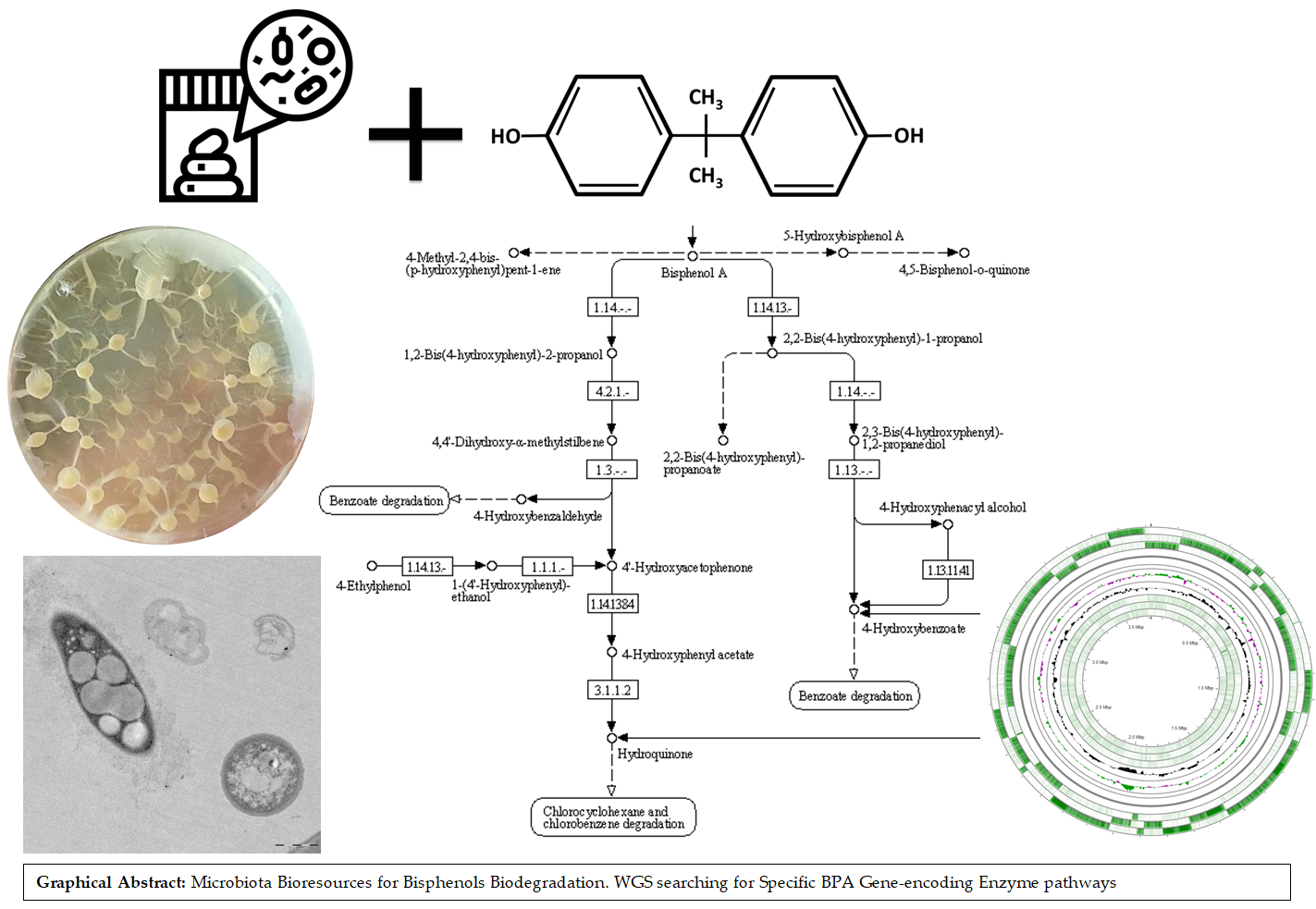
Microorganisms for BPA degradation with inulinase activityThis technology focuses on using bacteria within the Bacillus spp species, which are capable of degradation and removal of BPA in addition to other endocrine disruptors, for the development of probiotic or enzymatic formula with use in health, feed and food, and/or the environmental industries.Unismart - University of Padua Foundation posted this:
Microplastic filter system for appliancesThis patented system approaches the problem by redesigning the entire discharge system of the washing machine, including the centrifugal pump and tube geometry.Universidad de Alicante posted this:
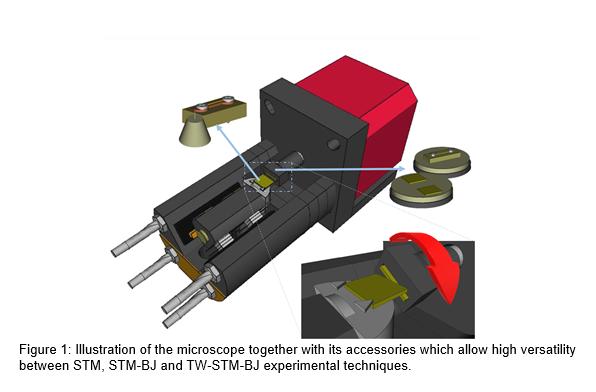
Microscope for twistronics and spintronics studiesResearchers from the Nanophysics group, from the Department of Applied Physics at the University of Alicante, have developed a microscope whose structure and assembly allows twistronics and spintronics studies to be carried out jointly. Specifically, it allows the development of topography studies with atomic resolution, electronic transport studies and spin studies with the possibility of angular variation. This invention, manufactured by 3D printing, stands out for its versatility, easy assembly, low price and adaptability to different experimental techniques. The group is looking for companies or institutions interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation.