Showing 1 to 15 of 2456 results


Emulsified suspensions for cold accumulation
Patents for licensing UATEC - Unidade de Transferência de Tecnologia

Rehabilit-AR: Augmented Reality for Rehabilitation
Innovative Products and Technologies UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS

Automated multi sensory rooms
Innovative Products and Technologies UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS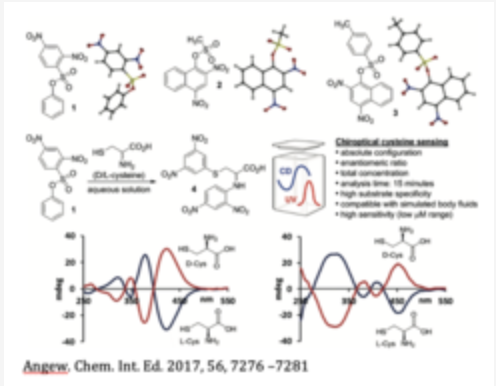

Probes for determining the absolute configuration of D/L-cysteine and/or the enantiomeric composition of cysteine in a sample.
Innovative Products and Technologies Georgetown University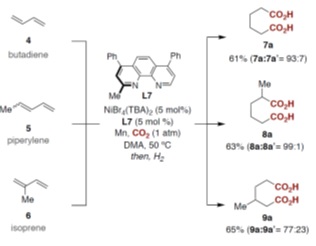

Adipic acid(s) prepared by catalytic carboxylation of 1,3-butadiene
Patents for licensing Institut Català d'Investigació Química (ICIQ)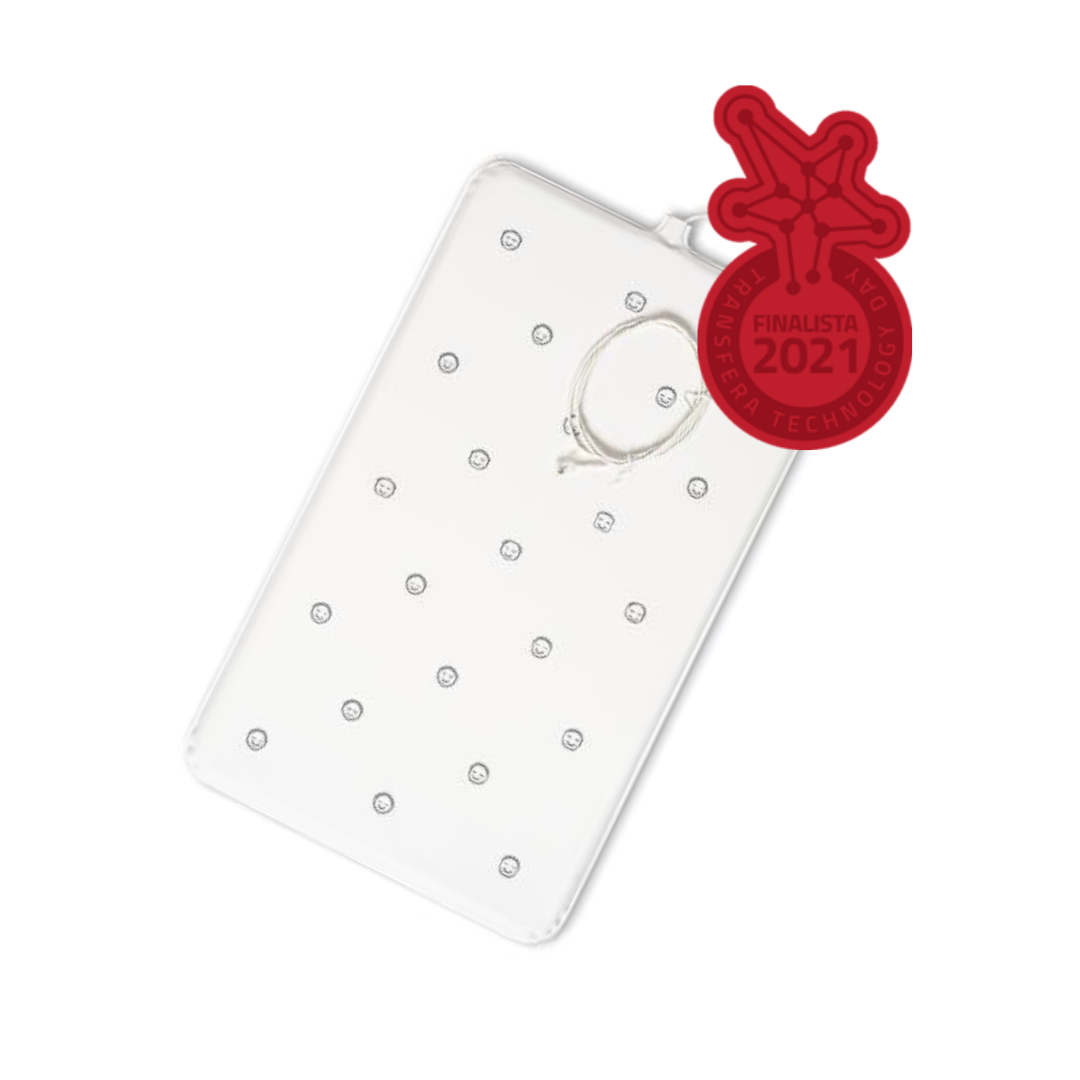

Fetal Activity Monitor - A system of sensors placed under the mattress of the pregnant women which monitors fetal activity
Innovative Products and Technologies University Hospital Hradec Králové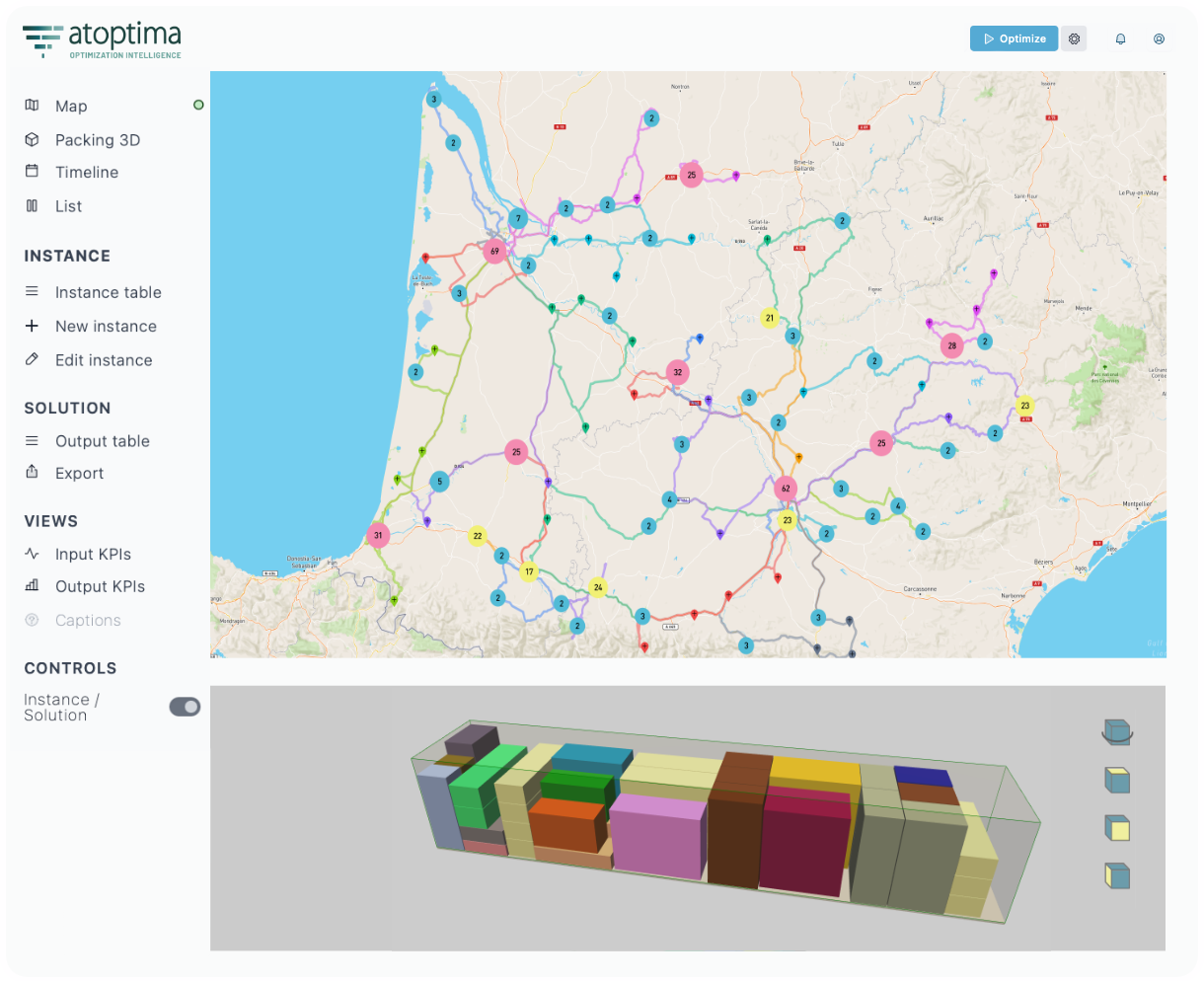

Suite of Optimization Solvers for Operations Planning
Innovative Products and Technologies Atoptima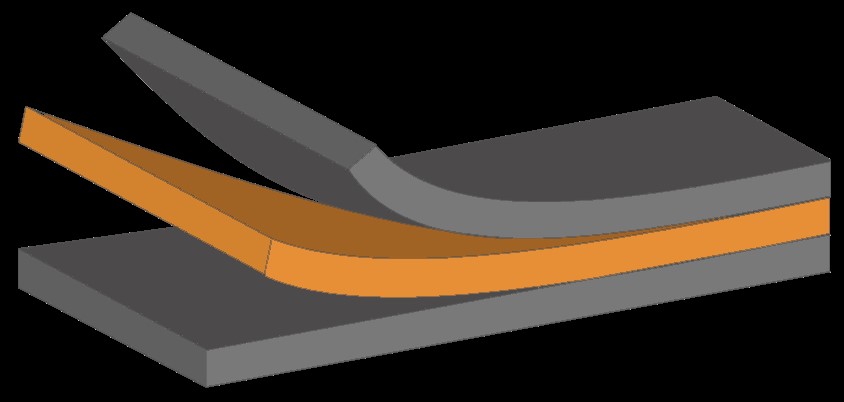

Multilayer film delamination process
Patents for licensing Universidad de Alicante

GATLING CORP - Load test as code
Innovative Products and Technologies EIT Digital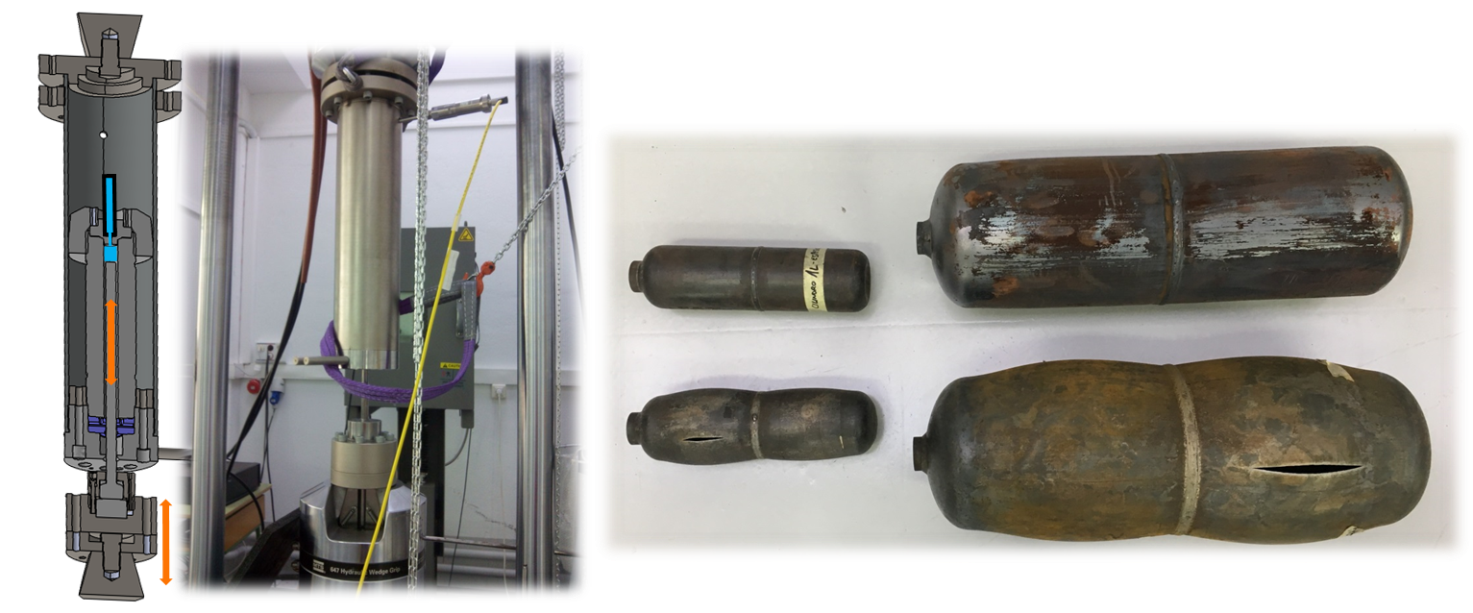

A device for the evaluation of the stuctural integrity of pipes and conduction elements subjected to high pressure.
Innovative Products and Technologies UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS

Ezrin Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment
Innovative Products and Technologies Georgetown University

Antimicrobial Coating for Face Masks and Self-Sanitizing Surfaces
Innovative Products and Technologies University of Alberta, Technology Transfer Services

High-temperature multivariable microwave sensors for Oil-Sand applications
Patents for licensing University of Alberta, Technology Transfer Services

A new early diagnostic procedure to breast cancer.
Patents for licensing Pragmatec