CSIC and CIBER have revealed a new role for acid ceramidase (ACDase) in experimental models and in patients with Niemann Pick type C disease that reduces cholesterol in mitochondrial membranes and oxidative stress.
Industrial partners from pharmaceutical industry are sought to collaborate through a patent licence
agreement.
ACDase to recover mitochondrial function
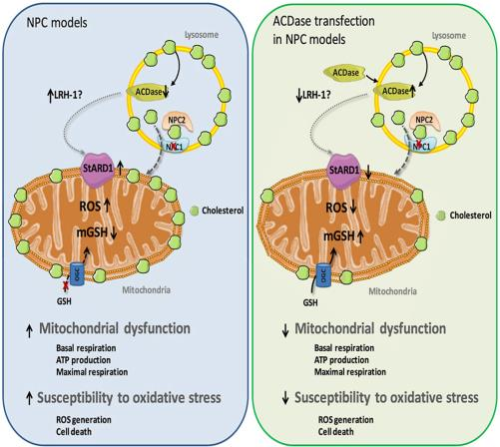
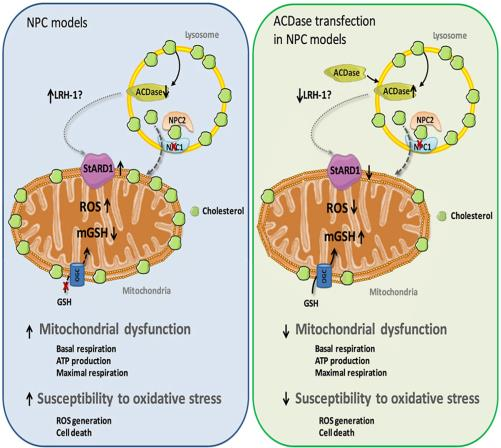
Acid ceramidase improves mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in Niemann-Pick type C disease Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are a group of inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function. Niemann–Pick type C disease (NPC) is a subgroup of LSDs characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and sphingolipids in the lysosomes of various tissues, mainly brain and liver, which causes neurological deterioration and liver disease.
This accumulation is due to an induction of the STARD1 protein, responsible for the transport of cholesterol to the mitochondrial inner membrane. The efficacy of most of the therapies available for patients with LSDs is limited, particularly because the treatments are usually initiated when organ damage has already occurred. Therefore, alternate targets for the treatment of NPC are required.
Presented here is the therapeutic use of acid ceramidase (ACDase), which inhibits STARD1 expression levels leading to the reduction of cholesterol in mitochondrial membranes and improving the performance and oxidative stress of fibroblasts of patients with NPC. Demonstrated action in in vivo models and in NPC patient samples.
Main innovations and advantages
· The therapeutic use of ACDase recovers mitochondrial function andreduces oxidative stress in samples of patients with NPC.
· Currently, targeted therapies in NPC disease focus on preventing theaccumulation of cholesterol in affected tissues. The proposed strategyis aimed at preventing the consequences caused by its accumulation inthe mitochondria, independently of the cholesterol alteration level.
· The action of ACDase maintains adequate mitochondrial function.