Never miss an update from Larisa Sheloukhova
Create your free account to connect with Larisa Sheloukhova and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Background
Various diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, collagen diseases, and cancer are characterized by blood vessel damage or induced angiogenesis. However, there are no technologies that allow high-resolution non-invasive imaging of blood vessels. The techniques currently used in clinical settings require contrast agent administration and exposure to X-ray or expensive contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The present invention is a non-invasive blood vessel imaging device that is based on photoacoustic (PA) tomography (PAT) that utilizes light absorption of hemoglobin.
Technical Summary
The inventors developed a photoacoustic imaging (PAI) system equipped with a hemispherical detector array (HDA) receiving PA signals. Two prototypes were made, PAI-03 and PAI-04, utilizing 795 nm, and 756 + 797nm wavelengths respectively
(Matsumoto et al. 2018). PAI-04 is an enhanced version with better specifications to ensure large-area, high-resolution blood vessel analysis (Fig. 1). The system allows for a spatial resolution of 0.27 mm and to distinguish arteries and veins by evaluating hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SO2).
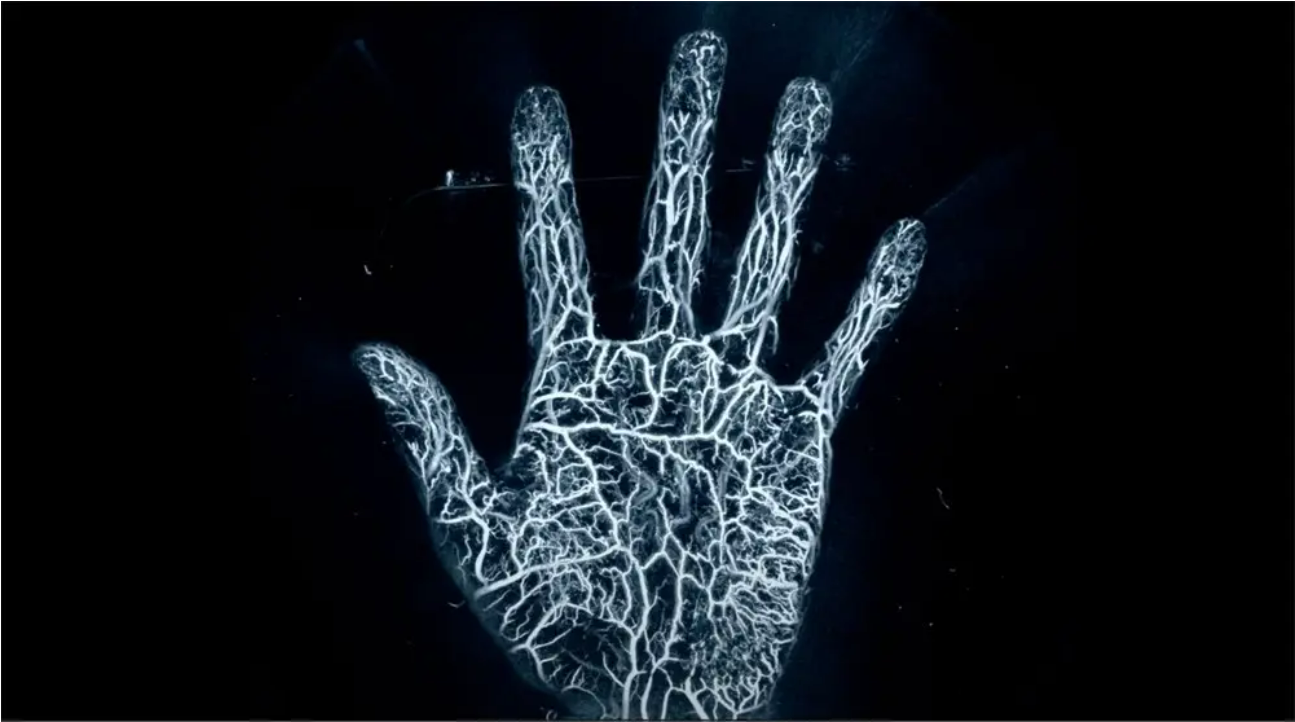
Figure 1. Non-invasive, ultra-high-resolution 3D image of blood vessels is obtained.
➤ Breast cancer diagnosis and flap reconstruction surgeries
The inventors have validated the system for breast cancer imaging and confirmed that small tumor-related blood vessels could be visualized. The device can be used in the clinical setting for differentiating between benign and malignant tumors,
monitoring drug treatment efficacy, as well as for mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Another application is preoperative planning for reconstruction flap surgeries. The device usage shortens operation time and reduces the risk of blood
flow disorders. The system’s design is also suitable for animal experiments, i.e. rodent vascular network can be visualized (Asao et al. 2023).
➤ Lymph vessels can also be visualized
The device can be used for lymph vessel imaging to perform a lymphatic venous anastomosis (LVA) super microsurgery for lymphedema. Unlike blood vessels, lymph vessel visualization requires the use of dye because lymph does not absorb light.
Luxonusis a start-upthat develops photoacoustic imaging systems for vascular vessel visualization.
Technology Readiness Level
7
Medical and non-medical scanners are available
Potential Applications
Possible Collaboration Mode(s)
Patent No
Pharmaceutical approval No. 30400BZX00212000 (Japan)
Publication(s)
Matsumoto Y, Asao Y, Sekiguchi H, Yoshikawa A, Ishii T, Nagae K-Iet al. Visualising peripheral arterioles and venules through high-resolution and large-area photoacoustic imaging.Sci Rep 2018;8: 14930.
Asao Y, Nagae K, Sekiguchi H, Aiso S, Watanabe S, Sato Met al. High-resolution photoacoustic 3D imaging system for animal experiments using a hemispherical detector array. In:Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing 2023. SPIE, 2023, pp 54–66.
Kyoto University was founded in 1897, the second university to be established in Japan. Kyoto University is among 10 National Designated Universities in Japan. It boasts 18 graduate schools, 10 faculties, 12 research institutes, and 26 centers and other establishments. Research conducted at Kyoto University spans the full spectrum of fields from social to natural science.
The outstanding research conducted at Kyoto University gives birth to useful technologies that could greatly benefit society. IAC (Office of Institutional Advancement and Communications) was established at Kyoto University to bridge the gap between researchers and industry. We facilitate joint research, technology transfer, creation of university startups, and provide entrepreneurial education. We are building a strong network of global industry partners to make sure basic research reaches the market.
Create your free account to connect with Larisa Sheloukhova and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Larisa
Technology Offers on Innoget are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Innoget is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Innoget support