Showing 1 to 15 of 2075 results


Method for predicting sex in fish
Patents for licensing CSIC - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas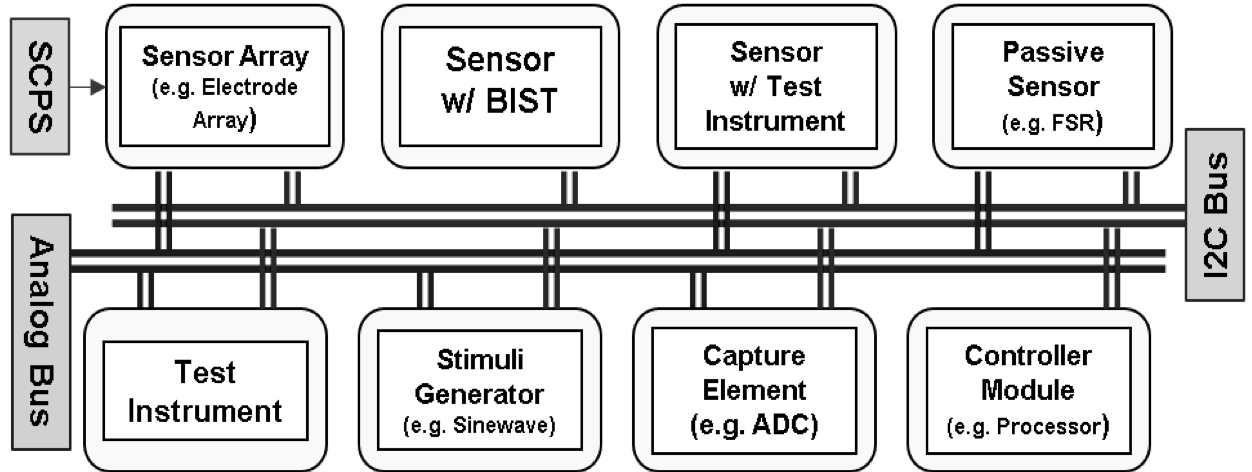

C4Mir - Control module for multiple mixed-signal resources management
Patents for licensing INESC TEC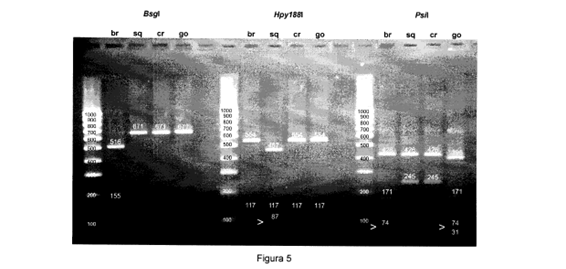

Procedure for the genetic identification of the european spices of the maja genero
Patents for licensing CINBIO

100% Organic Fuel Additive for petrol and diesel engines
Innovative Products and Technologies Laser Consult Ltd.

Rehabilit-AR: Augmented Reality for Rehabilitation
Patents for licensing UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS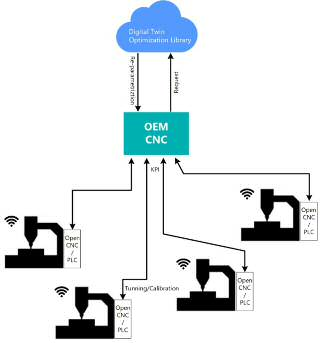

Intelligent device for the automatic parameterization through a digital twin of a
Patents for licensing Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas

Cargorotator.com - B2B online marketplace to reduce/avoid empty container trips
Innovative Products and Technologies HDC

Use of Homebrew Software
Patents for licensing UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS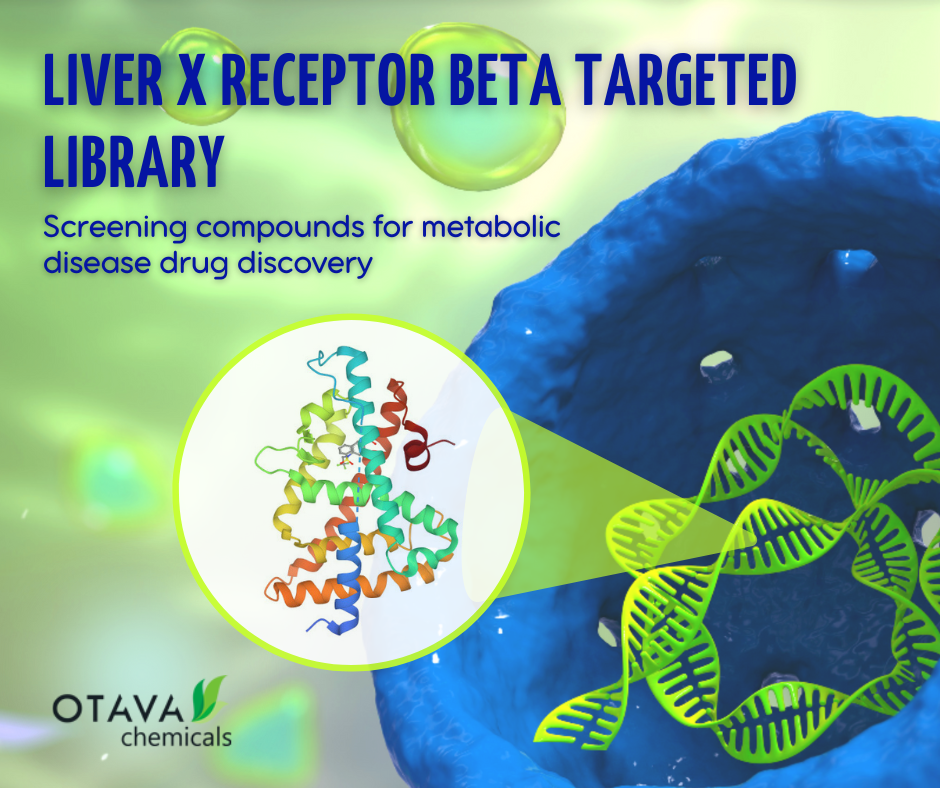

New Liver X receptor β Targeted Library
Innovative Products and Technologies Otava Research Institute

Bacterial nanocellulose biomaterial production
Patents for licensing Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas![New concept laboratories to analyse the human body movements using a combination of technologies depending on the parts of the bod[…]](https://static3.innoget.com/images/bgpremium.png)

New concept laboratories to analyse the human body movements using a combination of technologies depending on the parts of the bod[…]
Innovative Products and Technologies Other Side Mirror S.L.

Ergonomic and adjustable geometry swimming paddle and elastic deformation for recovery of energy
Patents for licensing FCPCT ULPGC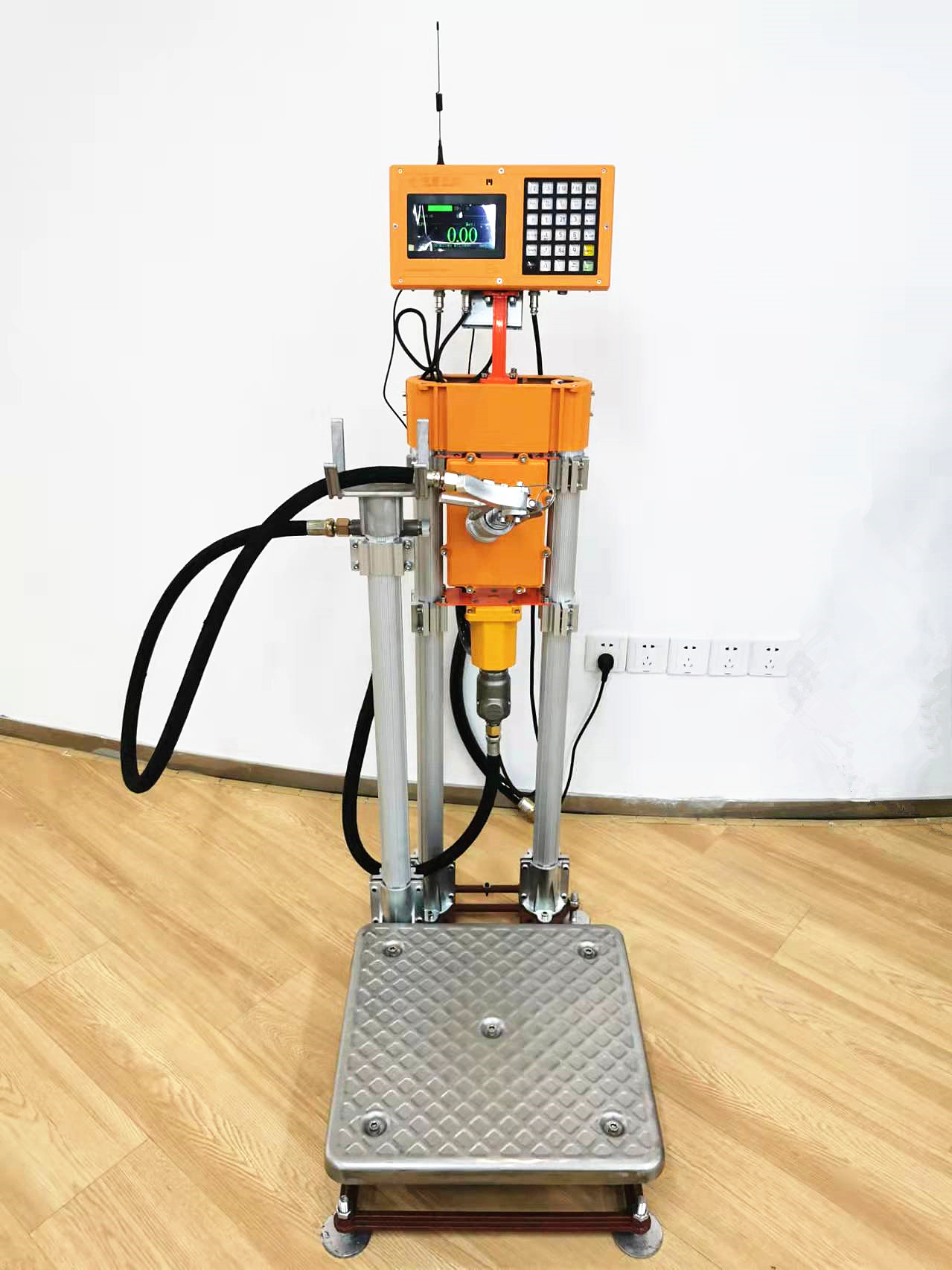

4G SIM card LPG Filling Machines to realize unfettered manage filling data anytime&anywhere
Innovative Products and Technologies XiangKang

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Of Tissue Fibrosis Without Contrast Agent
Patents for licensing Yeda

